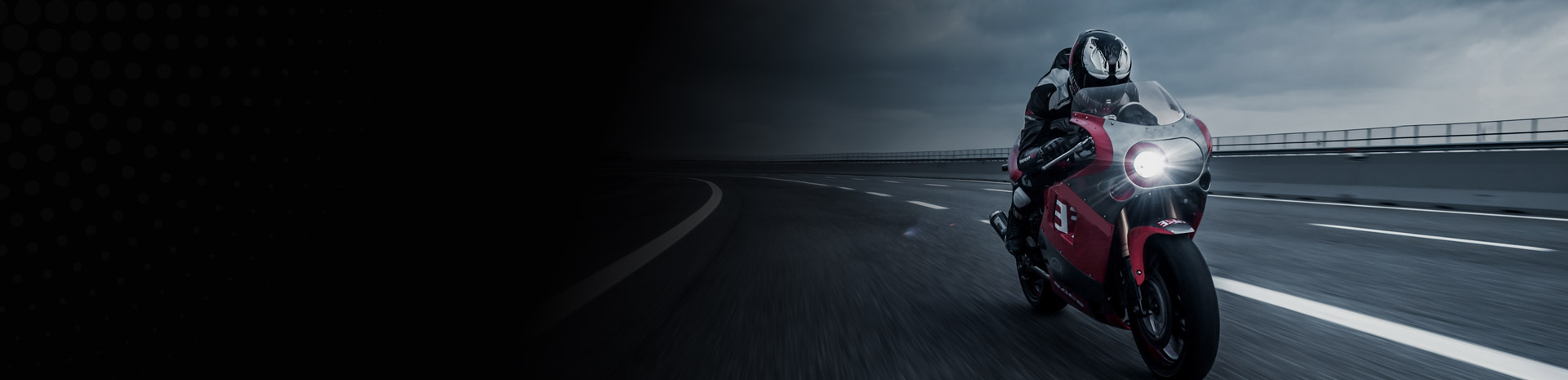
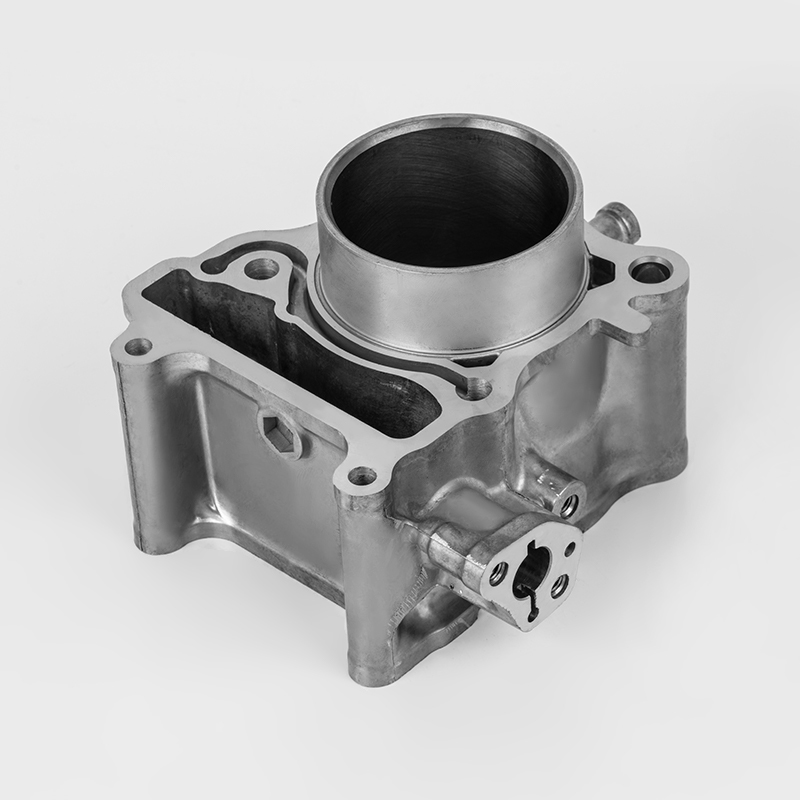
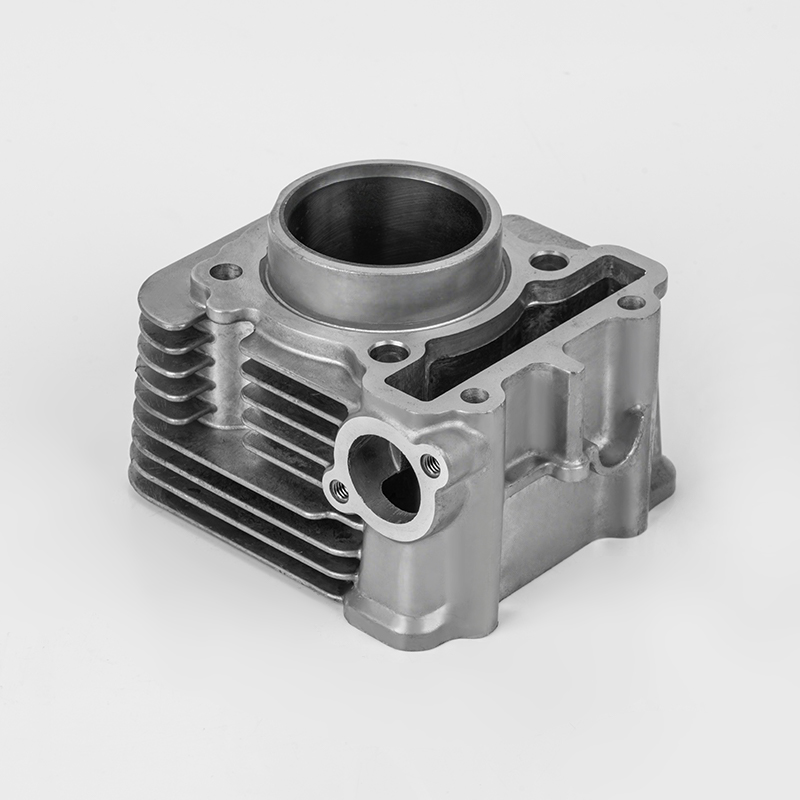
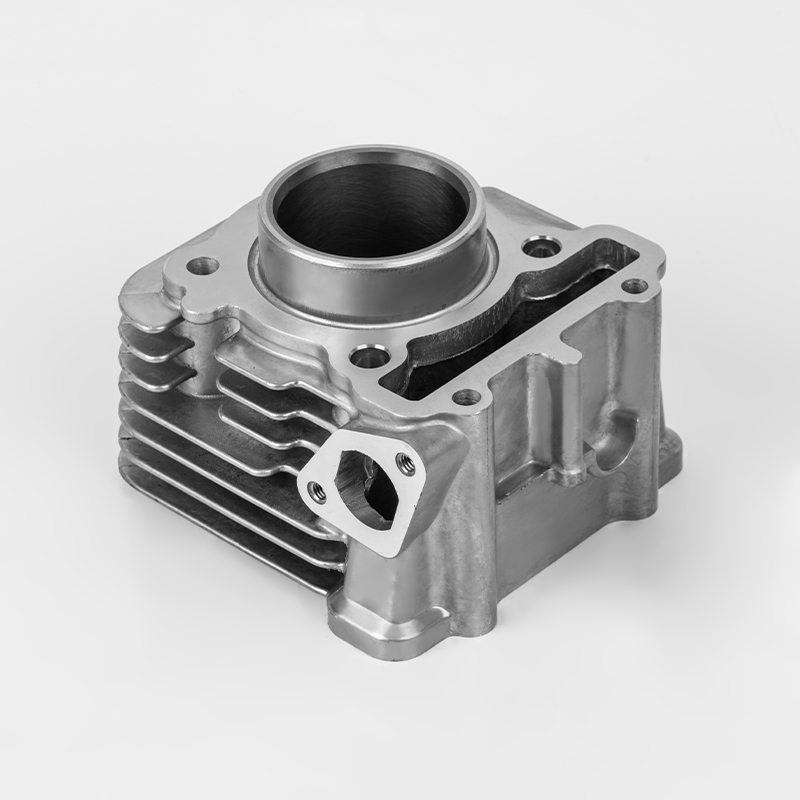
The lifespan of a 4-cylinder engine doesn't have a fixed number; it's more like a marathon than a sprint. How you treat it determines how long it will last. A well-maintained car can easily run for 200,000 or even 300,000 kilometers, and some can go even further.
Here are the key factors affecting how far your 4-cylinder engine will go:
Content
↗ Regular Maintenance is the Secret to Longevity
Timely Oil Changes: Engine oil is like the "blood" of the engine. Regularly changing the oil and filter is crucial for keeping internal parts running smoothly and reducing friction and wear. If the oil becomes dirty or deteriorates, friction increases, accelerating engine "aging."
Regular Inspections: Follow the car manufacturer's maintenance recommendations and regularly check the spark plugs, belts, and fluid levels. Fixing small problems promptly prevents them from escalating into major issues that could ruin the engine.
Cooling System: The engine generates a lot of heat during operation. The cooling system must function properly to ensure the engine doesn't overheat. Uncontrolled temperature can cause significant damage to the engine's internal components.
↗ Impact of Driving Habits
Gentle Driving: Smooth acceleration and deceleration, avoiding frequent hard acceleration or sudden braking, significantly reduces the strain on the engine (and transmission).
Steady Cruising: Maintaining a steady speed on the highway is more beneficial to the engine than frequent stop-and-go driving in the city.
Avoid Overloading: Don't subject your 4-cylinder engine to prolonged periods of high RPM and heavy load, such as towing excessively heavy objects for extended periods.
↗ Engine-Specific Factors
Design and Manufacturing: Some brands of engines are known for their durability from the design stage, often using stronger materials and more conservative tuning.
Turbocharging: While turbocharged engines offer more power, they typically operate under higher pressure and temperature, and theoretically may be slightly more "delicate" than naturally aspirated engines of the same type, requiring more meticulous maintenance.
Operating Environment: Frequently driving in dusty, extreme temperature (too cold or too hot) environments puts extra stress on the engine.


 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى