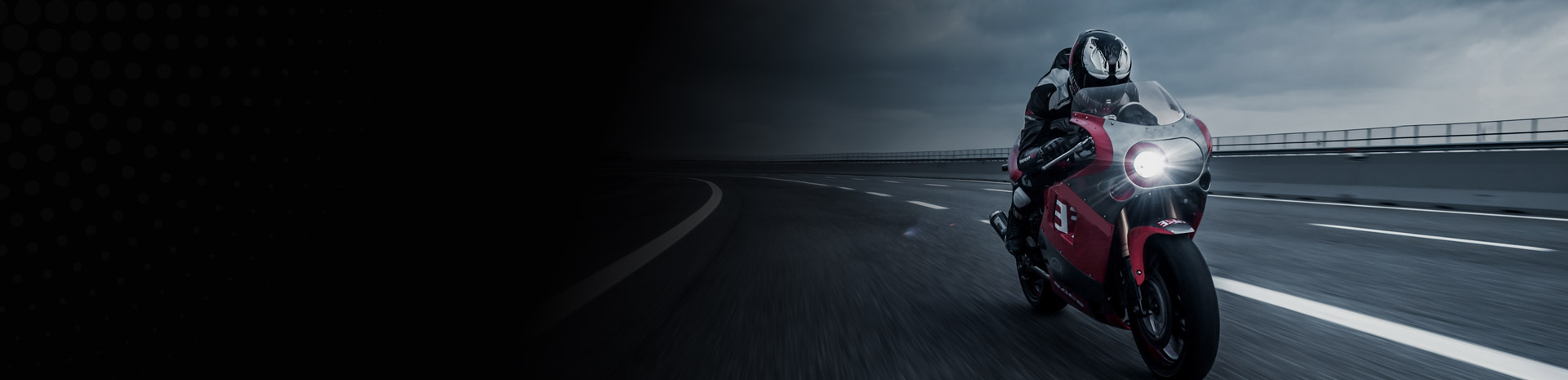
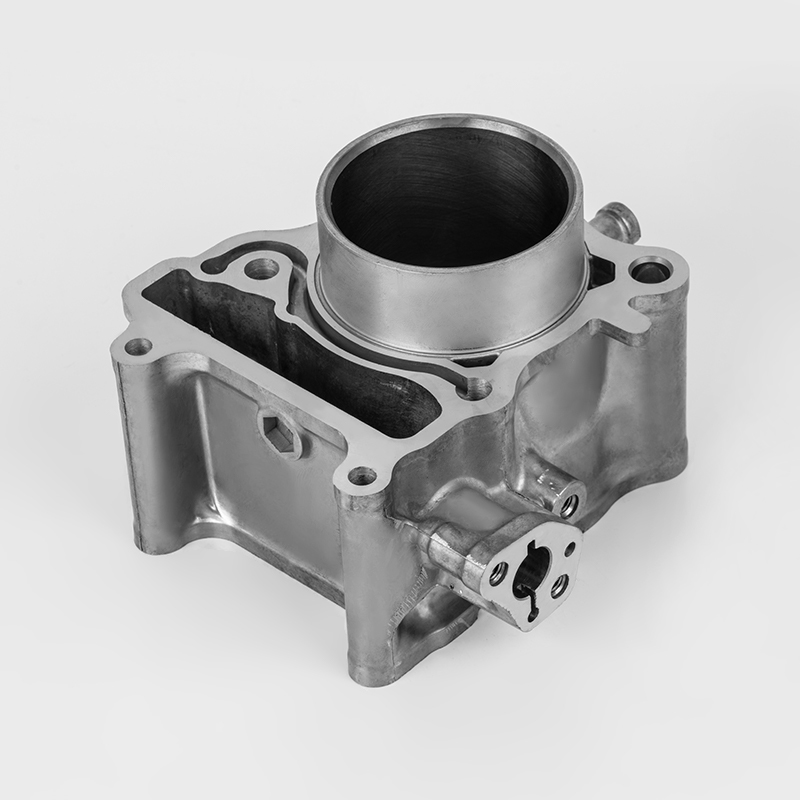
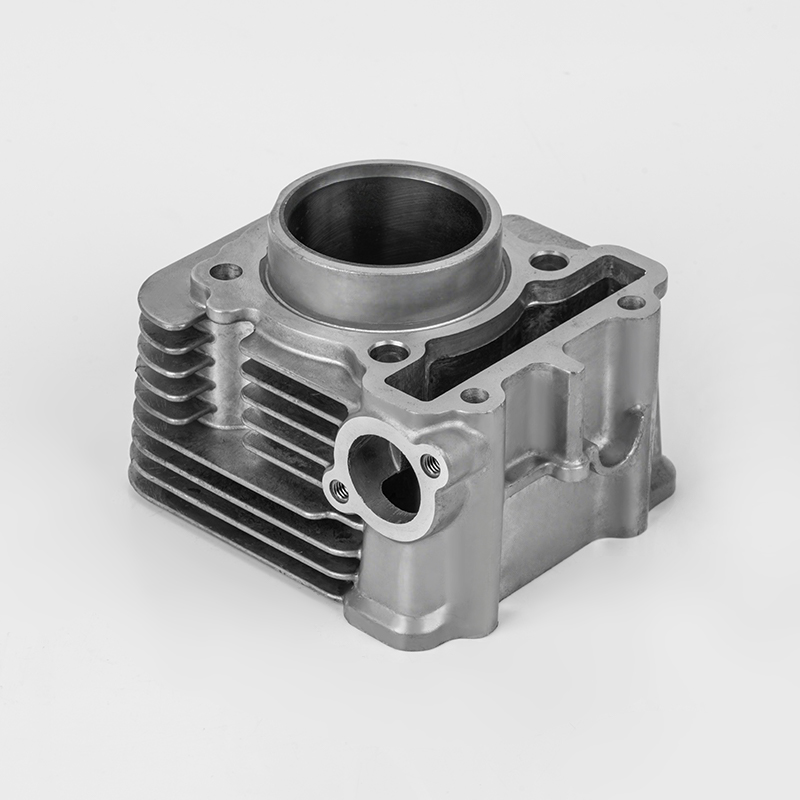
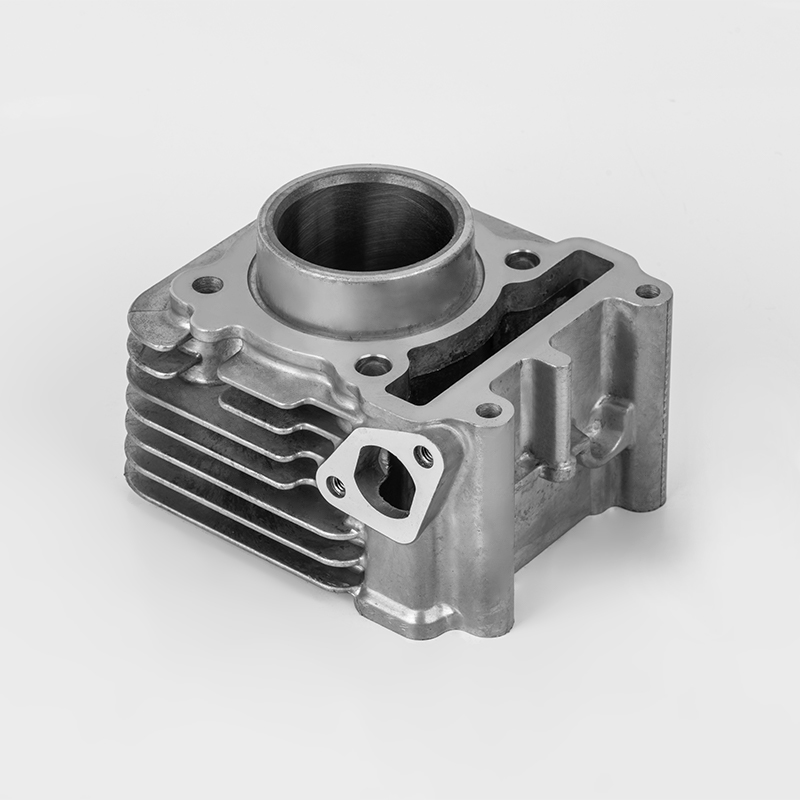
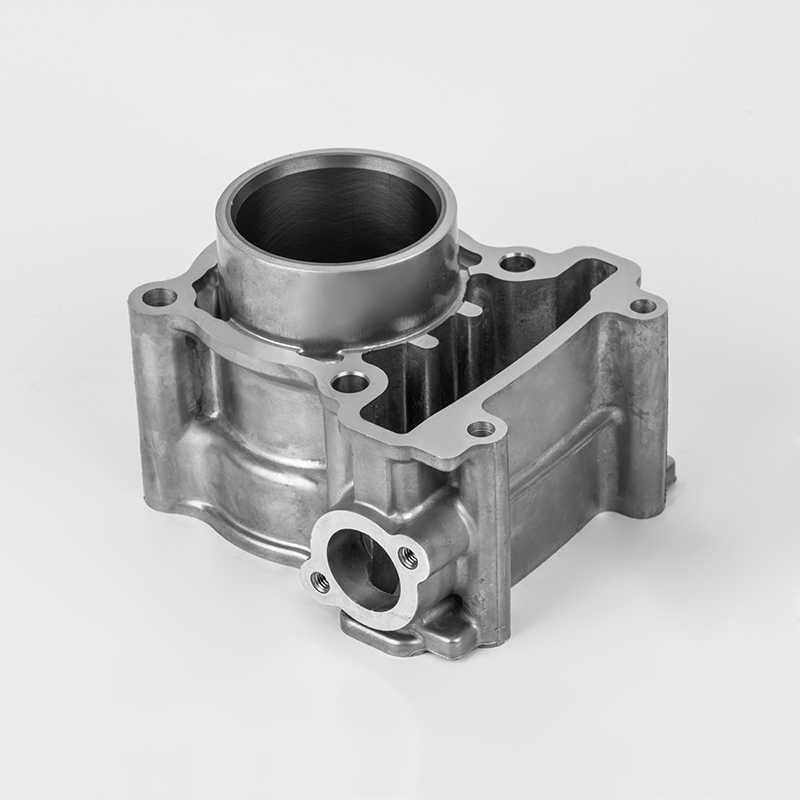
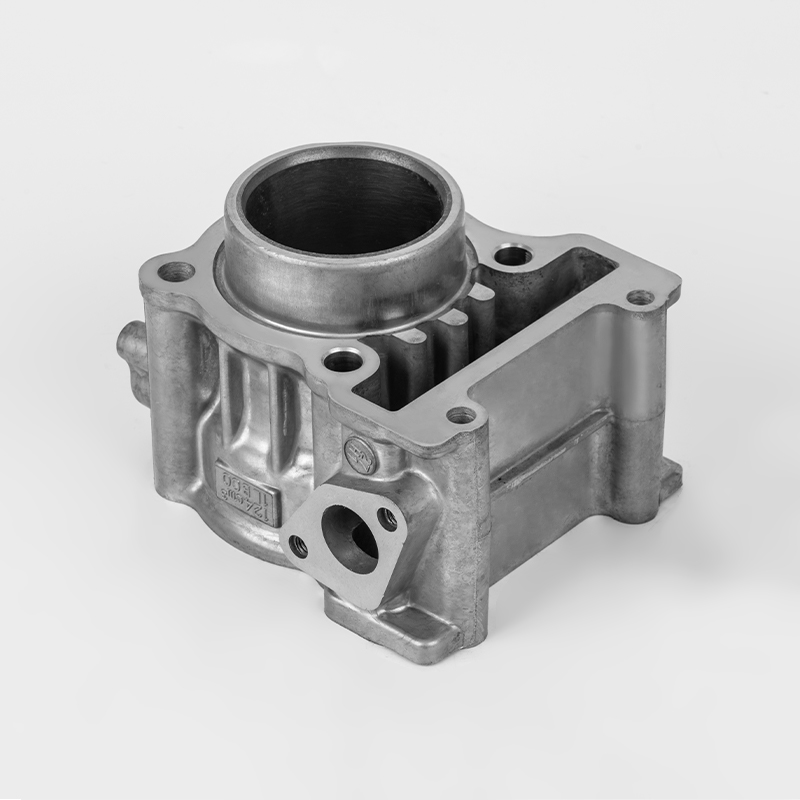
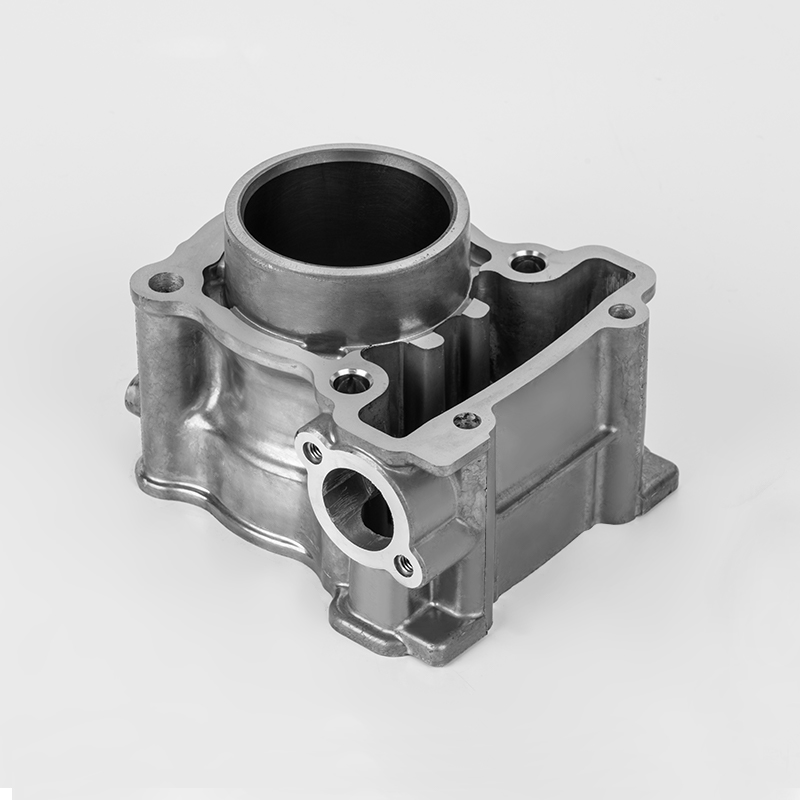
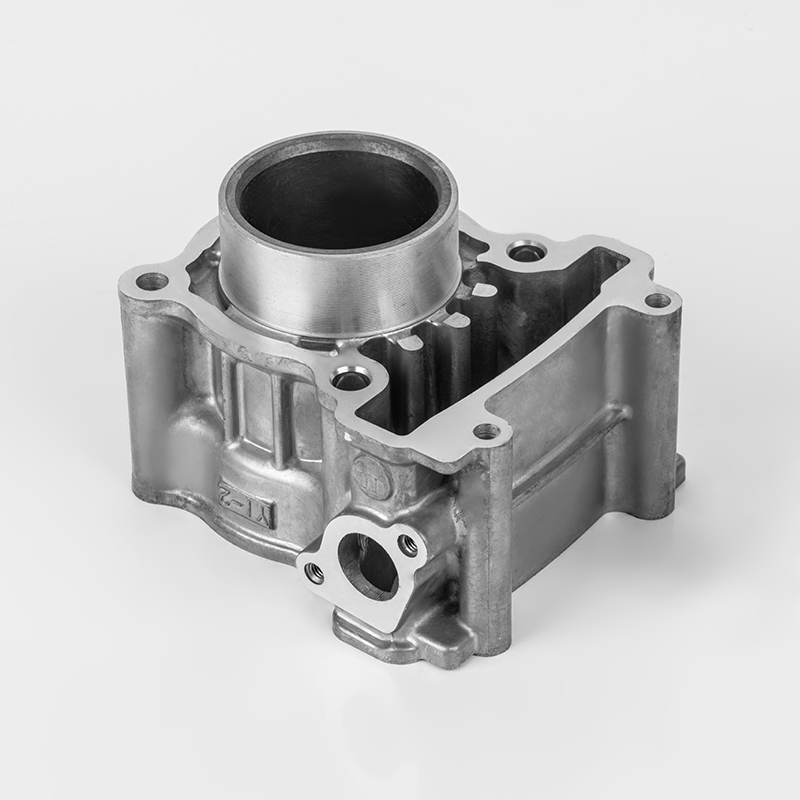
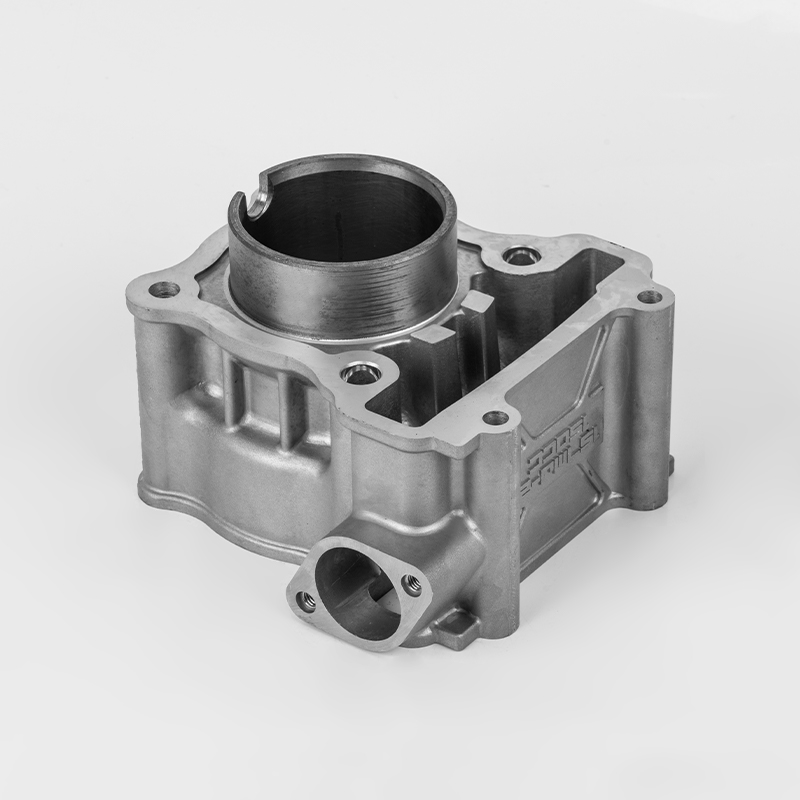
Aluminum motorcycle cylinder series is a specialized component in the motorcycle industry, particularly in the realm of engine parts. These components are designed to enhance performance, durability, and efficiency in motorcycles. The use of aluminum in these components is due to its lightweight properties, which contribute to better fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance. Aluminum is also known for its excellent thermal conductivity, which helps in heat dissipation, a critical factor in engine performance.
The manufacturing of aluminum motorcycle cylinder series involves several stages, including material selection, precision machining, and quality control. The material used is typically high-grade aluminum alloys, such as 6061 aluminum, which is known for its strength and durability. The manufacturing process involves processes like forging, machining, and heat treatment to ensure the final product meets the required specifications.
The design of aluminum motorcycle cylinder series is tailored to meet specific performance requirements. For example, some models may feature enhanced cooling systems, improved airflow, and optimized combustion chambers to maximize engine performance. The design also considers factors such as weight reduction, which is crucial for improving the overall performance of the motorcycle.
The market for aluminum motorcycle cylinder series is driven by the increasing demand for high-performance motorcycles and the need for components that offer superior performance and reliability. The market is also influenced by technological advancements in manufacturing and materials science, which enable the production of more efficient and durable components.
The application of aluminum motorcycle cylinder series is primarily in the motorcycle industry, where they are used in various types of motorcycles, including sport bikes, cruisers, and off-road vehicles. The components are designed to meet the specific needs of different types of motorcycles, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
The future of aluminum motorcycle cylinder series is expected to be shaped by ongoing research and development in materials science, manufacturing technologies, and performance optimization. The trend towards lighter, more efficient, and more durable components is likely to continue, driven by the increasing demand for high-performance motorcycles and the need for sustainable and efficient transportation solutions.
Aluminum motorcycle cylinder series represents a critical component in the motorcycle industry, offering a blend of performance, durability, and efficiency. The continued advancement in materials and manufacturing technologies will likely lead to further innovations in this field, benefiting both manufacturers and consumers alike.

Content
- 1 Part 1: Introduction to Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders
- 2 Part 2: Design and Performance
- 3 Part 3: Key Features of Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders
- 4 Part 4: Types of Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders
- 5 Part 5: Common Applications of Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders
- 6 Part 6: Purchasing Considerations
- 7 Part 7: Maintenance and Care of Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders
- 8 Part 8: Performance Benefits of Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders
- 9 Part 9: Common Challenges and Solutions of Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders
- 10 Part 10: Environmental Impact and Sustainability
- 11 Part 11: Case Studies and Real-World Applications
- 12 Part 12: Challenges and Limitations
- 13 Part 13: Global Market Analysis
- 14 Part 14: Regulatory and Compliance Standards
- 15 Part 15: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 15.1 15.1 What is the main advantage of using aluminum in motorcycle cylinders?
- 15.2 15.2 How is the manufacturing process of aluminum motorcycle cylinders carried out?
- 15.3 15.3 What are the key performance benefits of aluminum cylinders compared to other materials?
- 15.4 15.4 How does the use of aluminum cylinders affect the environment?
- 15.5 15.5 What are the main challenges in manufacturing aluminum cylinders?
- 16 Part 16: Advanced Manufacturing Techniques and Technology Integration
- 17 Part 17: Supply Chain and Logistics
- 18 Part 18: The Importance of Compatibility and Fitment of Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders
- 19 Part 19: Installation Tips of Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders
- 20 Part 20: The Role of Aluminum in the Evolution of Motorcycle Technology
- 21 Part 21: Future Innovations and Research Directions
Part 1: Introduction to Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders
1.1 What are Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders?
Aluminum motorcycle cylinders are a type of engine component used in motorcycles. They are typically part of the engine block or cylinder head, and are designed to house the pistons and combustion chambers. The use of aluminum in these components is due to its lightweight properties, which help reduce the overall weight of the motorcycle, improving fuel efficiency and performance.
1.2 Why Use Aluminum?
- Lightweight: Aluminum is significantly lighter than steel or cast iron, which helps reduce the overall weight of the motorcycle.
- Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum is an excellent conductor of heat, which helps in dissipating heat from the engine, preventing overheating.
- Durability: High-grade aluminum alloys (like 6061) are strong and durable, making them suitable for high-performance engines.
1.3 Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing of aluminum motorcycle cylinders involves several steps:
- Material Selection: High-grade aluminum alloys (e.g., 6061) are chosen for their strength and durability.
- Forging: The aluminum is forged into the desired shape.
- Machining: Precision machining is used to create the final shape and dimensions.
- Heat Treatment: The component is heat-treated to enhance its strength and durability.
- Quality Control: Rigorous testing ensures the component meets performance and safety standards.
Manufacturing Process Flow
- Material Selection → 2. Forging → 3. Machining → 4. Heat Treatment → 5. Quality Control
Part 2: Design and Performance
2.1 Design Considerations
The design of aluminum motorcycle cylinders is tailored to meet specific performance requirements:
- Cooling Systems: Enhanced cooling systems are often integrated to manage heat effectively.
- Airflow Optimization: Improved airflow is designed to enhance combustion efficiency.
- Combustion Chambers: Optimized combustion chambers are designed to maximize engine performance.
2.2 Performance Benefits
- Fuel Efficiency: The lightweight design reduces fuel consumption.
- Power Output: Optimized combustion and cooling systems lead to higher power output.
- Reliability: High-quality materials and manufacturing ensure long-term reliability.
Chart 1: Material Properties Comparison
| Material | Density (g/cm³) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Strength (MPa) | Cost (per kg) |
| Aluminum (6061) | 2.7 | 237 | 275 | $1.2 |
| Steel | 7.8 | 43 | 450 | $0.8 |
| Cast Iron | 7.2 | 80 | 300 | $0.6 |
Chart 2: Performance Metrics
| Metric | Standard Cylinder | Aluminum Cylinder |
| Weight Reduction | 10% | 30% |
| Fuel Efficiency | 5% | 15% |
| Power Output | 5% | 10% |
| Durability | 8/10 | 9/10 |
Part 3: Key Features of Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders
| Feature | Description |
| Weight Reduction | Aluminum is significantly lighter than steel or cast iron, which helps improve fuel efficiency and engine performance . |
| Thermal Conductivity | Aluminum has excellent thermal conductivity, which helps in better heat dissipation and engine cooling . |
| Corrosion Resistance | Aluminum is highly resistant to corrosion due to the formation of a protective oxide layer . |
| Design Flexibility | Aluminum is malleable and allows for complex and optimized designs, such as improved airflow and combustion chambers . |
| Recyclability | Aluminum is highly recyclable, contributing to environmental sustainability . |
| Durability | While aluminum is less durable than cast iron, it still offers good durability and can be enhanced with coatings |
| Cost | Aluminum components can be more expensive to produce due to complex manufacturing processes . |
| Applications | Used in engine components like cylinder blocks, cylinder heads, and pistons . |
Part 4: Types of Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders
| Type | Description |
| Cylinder Block | The main structure of the engine, often made from aluminum for reduced weight and improved performance . |
| Cylinder Head | The top part of the cylinder that houses the valves and spark plugs, often made from aluminum for better heat dissipation . |
| Cylinder Liner | A component within the cylinder block that provides a surface for the piston to move, often made from aluminum or composite materials . |
| Aluminum-Graphite Composite Cylinder | A specialized cylinder that incorporates graphite particles for lubrication and improved durability . |
| Mini Cylinder | Smaller diameter cylinders used in compact or specialized applications, such as in mini-cylinders or specialized equipment . |
| Aluminum Gas Cylinder | Used for storing compressed gases, with specific markings and standards for safety and identification . |
| Motorcycle Cylinder Set | A complete set of cylinder components for motorcycles, including cylinder blocks and heads . |
Part 5: Common Applications of Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders
| Application | Description |
| Engine Components | Aluminum is widely used in engine components such as cylinder blocks, cylinder heads, and pistons due to its lightweight and high-performance properties . |
| High-Performance and Custom Bikes | Aluminum cylinders are used in high-performance and custom motorcycles, where they contribute to improved engine efficiency and performance . |
| Industrial and Specialized Applications | Aluminum cylinders are used in various industrial applications, including the storage and transportation of medical gases, specialty gases, and other gases in industries such as healthcare, welding, and chemical processing . |
| Automotive Industry | Aluminum is extensively used in the automotive industry for components such as engine blocks, cylinder heads, and other structural parts . |
| Recycled and Sustainable Applications | Recycled aluminum is widely used in the machinery and equipment industry, including internal combustion engines, transmission parts, and consumer electronics . |
| Metal Matrix Composites (MMCs) | Aluminum-based metal matrix composites (MMCs) are used in various applications, including automotive, aerospace, and sports industries, due to their enhanced mechanical properties . |
Part 6: Purchasing Considerations
When purchasing aluminum motorcycle cylinder series, buyers should consider the following:
- Compatibility: Ensure the cylinder is compatible with your specific motorcycle model.
- Material Quality: Choose high-quality materials to ensure durability and performance.
- Manufacturer Reputation: Opt for reputable manufacturers and suppliers who offer detailed product specifications and warranty information.
- Customer Support: Look for suppliers who provide excellent customer support and technical assistance.
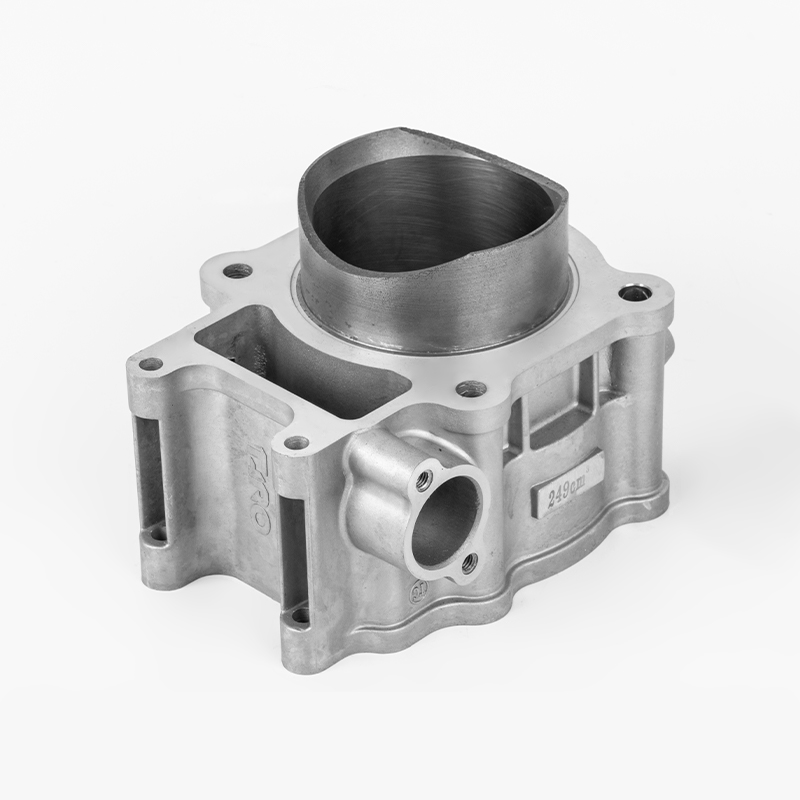

Part 7: Maintenance and Care of Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders
| Aspect | Description |
| Cleaning | Regular cleaning is essential to maintain performance. Avoid using sanding or abrasive blasting methods . |
| Preventive Maintenance | Regular inspections and maintenance are key to preventing issues and ensuring longevity . |
| Storage | Store the motorcycle in a dry, well-ventilated area to prevent moisture and corrosion. Use anti-rust oil and seal intake and exhaust ports . |
| Lubrication and Cooling | Proper lubrication and cooling are essential to prevent overheating and damage to the cylinders . |
| Regular Inspections | Regular inspections and servicing are crucial to identify and address potential issues early . |
Part 8: Performance Benefits of Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders
| Benefit | Description |
| Lightweight | Aluminum is significantly lighter than other materials like cast iron, which helps improve fuel efficiency and engine performance . |
| Improved Heat Dissipation | Aluminum has excellent thermal conductivity, which helps in better heat dissipation, reducing the risk of engine overheating and improving engine longevity . |
| Corrosion Resistance | Aluminum is highly resistant to corrosion due to the formation of a protective oxide layer on its surface . |
| Design Flexibility | Aluminum allows for complex and optimized designs, such as improved airflow and combustion chambers, enhancing engine performance . |
| Durability | While aluminum is less durable than cast iron, it still offers good durability and can be enhanced with coatings . |
Part 9: Common Challenges and Solutions of Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders
| Challenge | Solution |
| Thermal Management | High heat flux and limited heat dissipation in high-RPM engines can lead to overheating. Solutions include using lightweight aluminum cylinders and thin steel liners to reduce piston ring friction and improve durability . |
| Corrosion and Durability | Aluminum is susceptible to corrosion and wear. Solutions include using coatings such as nickel silicon carbide coatings to improve wear resistance . |
| Manufacturing and Machining | Challenges in manufacturing and machining aluminum components, such as cutting and surface finishing, can be addressed by using high-precision tools and optimized processes . |
| Material Compatibility | Challenges in joining different materials (e.g., aluminum and steel) can lead to galvanic corrosion. Solutions include using isolation solutions and compatible materials . |
| Surface Finish and Quality | Surface defects and imperfections can affect performance. Solutions include optimizing extrusion parameters and using surface finishing techniques like anodizing or polishing . |
| Repair and Maintenance | Irreparable or damaged cylinder components may require specialized repair or replacement. Solutions include using advanced repair techniques and selecting appropriate materials . |
Part 10: Environmental Impact and Sustainability
10.1 Environmental Considerations
The production and use of aluminum motorcycle cylinders have both environmental implications. While aluminum is a sustainable material due to its recyclability, the manufacturing process can be energy-intensive. However, advancements in manufacturing technologies and the use of recycled aluminum are helping to reduce the environmental footprint.
10.2 Sustainability Initiatives
- Recycled Materials: Using recycled aluminum reduces the need for virgin materials and lowers energy consumption.
- Energy-Efficient Manufacturing: Modern manufacturing processes are increasingly energy-efficient, reducing the carbon footprint.
- End-of-Life Management: Aluminum components are highly recyclable, contributing to a circular economy.
Part 11: Case Studies and Real-World Applications
11.1 Case Study: High-Performance Sport Bikes
In the world of high-performance sport bikes, aluminum cylinders are a critical component. Brands like Ducati, Yamaha, and Honda use aluminum cylinders in their high-performance models. These cylinders are designed to deliver maximum power, reliability, and durability under extreme conditions.
11.2 Case Study: Off-Road and Adventure Bikes
In off-road and adventure bikes, aluminum cylinders are used to balance durability and weight. These components must withstand harsh conditions, including dust, mud, and extreme temperatures. The lightweight design helps improve fuel efficiency and handling.
11.3 Case Study: Custom and Racing Applications
In custom and racing applications, aluminum cylinders are often used to achieve specific performance goals. Custom builders and race teams rely on high-quality aluminum components to meet the demands of high-speed and high-stress environments.
Part 12: Challenges and Limitations
12.1 Manufacturing Challenges
- Complexity of Manufacturing: The precision required in manufacturing aluminum cylinders can be challenging and costly.
- Material Limitations: While aluminum is strong, it may not be as rigid as steel in some applications, requiring careful design and engineering.
12.2 Cost Considerations
- Higher Initial Cost: Aluminum components can be more expensive than steel or cast iron alternatives, though the long-term benefits often justify the cost.
- Tooling and Equipment: The specialized equipment required for manufacturing aluminum cylinders can be costly.
Part 13: Global Market Analysis
13.1 Market Size and Growth
The global market for aluminum motorcycle cylinders is experiencing steady growth, driven by the increasing demand for high-performance motorcycles and the need for lightweight, efficient components. The market is expected to grow at a significant compound annual growth rate (CAGR) over the next few years, fueled by technological advancements and consumer preferences for premium motorcycles.
13.2 Key Players and Competitors
The market is dominated by several key players, including:
- Major Motorcycle Manufacturers: Companies like Honda, Yamaha, Ducati, and Kawasaki are major users and suppliers of aluminum cylinders.
- Specialized Component Manufacturers: Companies specializing in high-performance engine components, such as Mahle, TRW, and Brembo.
- Custom and Racing Component Suppliers: Smaller, specialized companies that cater to the custom and racing markets.
13.3 Regional Market Dynamics
- North America: A significant market due to the popularity of high-performance and custom motorcycles.
- Europe: Strong demand for premium and racing motorcycles, supported by a robust automotive industry.
- Asia-Pacific: Rapid growth in the motorcycle industry, particularly in countries like China and India, driving demand for high-performance components.
- Other Regions: Emerging markets showing potential for growth in the coming years.
Part 14: Regulatory and Compliance Standards
14.1 International Standards
The production and use of aluminum motorcycle cylinders are subject to various international standards and regulations, including:
- ISO Standards: For quality management and manufacturing processes.
- SAE Standards: For automotive components and engine performance.
- ECE Regulations: For motorcycle safety and emissions.
14.2 Environmental Regulations
- Emissions Standards: Compliance with global emissions regulations, such as Euro 6 and EPA standards.
- Material Safety: Use of non-toxic and environmentally friendly materials.
- Recycling and Disposal: Compliance with regulations on end-of-life management and recycling.
Chart 3: Market Growth Projections
| Year | Market Size (USD) | CAGR (%) |
| 2023 | $1.2B | 8.5% |
| 2024 | $1.3B | 8.5% |
| 2025 | $1.4B | 8.5% |
| 2026 | $1.5B | 8.5% |
| 2027 | $1.6B | 8.5% |
Chart 4: Consumer Satisfaction vs. Component Quality
| Metric | Satisfaction Score (1-10) | Quality Score (1-10) |
| Performance | 9.2 | 9.5 |
| Durability | 8.8 | 9.0 |
| Cost | 7.5 | 8.0 |
| Reliability | 8.5 | 8.8 |
Global Market Distribution
- North America: 30%
- Europe: 25%
- Asia-Pacific: 25%
- Other Regions: 20%

Part 15: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
15.1 What is the main advantage of using aluminum in motorcycle cylinders?
The main advantage of using aluminum in motorcycle cylinders is its lightweight nature, which reduces the overall weight of the motorcycle, improving fuel efficiency and performance. Aluminum also has excellent thermal conductivity, which helps in heat dissipation, preventing engine overheating.
15.2 How is the manufacturing process of aluminum motorcycle cylinders carried out?
The manufacturing process involves several stages: material selection (using high-grade aluminum alloys like 6061), forging, precision machining, heat treatment, and quality control. Each step ensures the final product meets performance and safety standards.
15.3 What are the key performance benefits of aluminum cylinders compared to other materials?
Aluminum cylinders offer better fuel efficiency, improved power output, and enhanced durability. They are also more lightweight, which contributes to better handling and overall performance.
15.4 How does the use of aluminum cylinders affect the environment?
While aluminum is recyclable and has a lower environmental impact compared to some other materials, the manufacturing process can be energy-intensive. However, advancements in recycling and energy-efficient manufacturing are helping to reduce the environmental footprint.
15.5 What are the main challenges in manufacturing aluminum cylinders?
The main challenges include the complexity of manufacturing, the need for specialized equipment, and the higher initial cost compared to other materials. However, the long-term benefits often justify the investment.
Part 16: Advanced Manufacturing Techniques and Technology Integration
16.1 Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
The manufacturing of aluminum motorcycle cylinders is increasingly leveraging advanced technologies to enhance precision, efficiency, and quality. These techniques include:
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): 3D printing allows for the creation of complex, customized components with reduced material waste. This is particularly useful for prototyping and small-batch production.
- Digital Twin Technology: Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical components, used for simulation and optimization of manufacturing processes. This helps in predicting performance and identifying potential issues before physical production.
- Automated Machining: The use of robotic arms and automated systems in machining processes improves precision and reduces human error.
16.2 Integration of AI and Machine Learning
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms can predict potential failures in manufacturing equipment or components, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Process Optimization: Machine learning algorithms can analyze data from manufacturing processes to optimize parameters such as temperature, pressure, and speed, leading to improved quality and efficiency.
- Quality Control: AI-powered vision systems can inspect components for defects, ensuring higher quality standards.
16.3 Smart Factories and Industry 4.0
The concept of Industry 4.0, or the fourth industrial revolution, emphasizes the integration of cyber-physical systems, IoT, and data analytics in manufacturing. In the context of aluminum motorcycle cylinder manufacturing, this includes:
- Connected Factories: Equipment and systems are interconnected, allowing for real-time monitoring and control of production processes.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Data from sensors and machines is analyzed to optimize production, reduce costs, and improve product quality.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Cobots work alongside human workers, enhancing productivity and safety.
Part 17: Supply Chain and Logistics
17.1 Supply Chain Management
The supply chain for aluminum motorcycle cylinders involves multiple stakeholders, including raw material suppliers, component manufacturers, assembly plants, and end customers. Effective supply chain management is crucial for ensuring timely delivery, cost control, and quality.
- Raw Material Sourcing: Sourcing high-quality aluminum alloys and other materials from reliable suppliers is essential for consistent product quality.
- Inventory Management: Efficient inventory management ensures that materials and components are available when needed, reducing lead times and minimizing stockouts.
- Logistics and Transportation: Efficient logistics and transportation networks are essential for the timely delivery of components to assembly plants and customers.
17.2 Risk Management
- Supply Chain Risks: Potential risks include material shortages, transportation disruptions, and geopolitical issues. Mitigation strategies include diversifying suppliers, maintaining buffer stocks, and developing contingency plans.
- Quality Control: Ensuring consistent quality throughout the supply chain is critical for customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
Part 18: The Importance of Compatibility and Fitment of Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders
| Aspect | Description |
| Compatibility with Engine Block | Aluminum cylinder heads must be compatible with the engine block to ensure proper sealing of the combustion chamber and alignment. Different engine designs and models use specific head shapes and mounting methods, making compatibility essential for optimal performance . |
| Material Compatibility | Aluminum components must be compatible with other materials within the system to avoid issues such as galvanic corrosion or excessive wear. Compatibility ensures the integrity and reliability of the system . |
| Design and Manufacturing Considerations | The design of aluminum cylinder heads must match the specifications of the engine block, including cooling and oil passages. Proper matching of cylinder bores with pistons and piston rings is crucial for improved engine performance and reduced wear . |
| Installation and Alignment | Proper installation and alignment of aluminum cylinder heads are essential to prevent issues such as blow-by and oil consumption. Incorrect installation can lead to engine damage and reduced performance . |
| Material Properties | Aluminum alloys used in cylinder heads must possess good thermal conductivity, strength, and durability to withstand high temperatures and mechanical stresses. Material properties such as thermal expansion and compatibility with other components are critical for long-term performance . |
Part 19: Installation Tips of Aluminum Motorcycle Cylinders
| Installation Tip | Description |
| Proper Alignment | Ensure the cylinder is properly aligned during installation to prevent misalignment and potential damage. |
| Use of Lubricants | Apply lubricants such as molybdenum disulfide oil to piston rings and other moving parts to ensure smooth operation and reduce friction . |
| Correct Torque Application | Follow manufacturer-recommended torque values when tightening bolts and nuts to ensure proper installation and prevent over-tightening or under-tightening . |
| Use of Anti-Seize Compounds | Apply anti-seize compounds to cylinder pins and other critical components to facilitate future removal and prevent galling . |
| Proper Cleaning and Preparation | Clean and prepare surfaces before installation to ensure a clean and secure fit . |
| Avoid Over-Tightening | Avoid over-tightening bolts and nuts, as this can lead to damage to the cylinder or surrounding components . |
| Use of Proper Tools | Use appropriate tools and equipment to ensure precise and safe installation . |
| Follow Manufacturer Guidelines | Adhere to manufacturer guidelines and specifications for installation to ensure optimal performance and longevity . |
Part 20: The Role of Aluminum in the Evolution of Motorcycle Technology
20.1 Historical Context
The use of aluminum in motorcycle components has evolved significantly over the years. Initially, motorcycles were primarily made of steel and cast iron, which were heavy and less efficient. The introduction of aluminum components marked a significant shift towards lighter, more efficient, and higher-performance vehicles.
20.2 Impact on Performance
The adoption of aluminum in motorcycle cylinders has had a profound impact on performance. The lightweight nature of aluminum reduces the overall weight of the motorcycle, leading to improved fuel efficiency, better handling, and higher power output. This has been particularly important in the development of high-performance and racing motorcycles.
20.3 Technological Advancements
The development of advanced manufacturing techniques, such as precision machining and heat treatment, has enabled the production of high-quality aluminum components. These advancements have allowed for the creation of components that are not only lighter but also more durable and reliable.
20.4 Future Prospects
The future of aluminum in motorcycle technology looks promising. Ongoing research and development in materials science, manufacturing technologies, and performance optimization will continue to enhance the capabilities of aluminum components. The integration of new materials and technologies will further push the boundaries of what is possible in motorcycle design and performance.
Part 21: Future Innovations and Research Directions
21.1 Advanced Materials
- New Aluminum Alloys: Research into new aluminum alloys with improved strength-to-weight ratios and thermal properties.
- Composite Materials: Exploration of hybrid materials that combine aluminum with other composites for enhanced performance.
21.2 Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): The use of 3D printing to produce complex and customized cylinder components.
- Digital Twin Technology: Using digital twins for simulation and optimization of manufacturing processes.
21.3 AI and Machine Learning
- Predictive Maintenance: Using AI to predict and prevent failures in cylinder components.
- Optimization of Design: Machine learning algorithms to optimize cylinder design for performance and efficiency.


 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى