Content
- 1 Introduction: What is the Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series?
- 2 Part 1: Understanding the Basics of Motorcycle Cylinders
- 3 Part 2: The Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series: Buyer’s Guide
- 4 Part 3: Common Issues and Solutions of Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series
- 5 Part 4: Maintenance Tips of Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series
- 6 Part 5: Manufacturing Methods of Iron Motorcycle Cylinders
- 7 Part 6: Repair Tips of Iron Motorcycle Cylinders
- 8
- 9 Part 7: Applications and Use Cases of Iron Motorcycle Cylinders
- 10 Part 8: Advantages and Limitations of Iron Motorcycle Cylinders
- 11 Part 9: Maintenance Tips of Iron Motorcycle Cylinders
- 12 Part 10: Influencing Factors Longevity of Iron Motorcycle Cylinders
- 13 Part 11: Manufacturing Process of Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series
- 14
- 15 Part 12: Quality Control and Testing of Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series
- 16 Part 13: Performance Characteristics and Performance Metrics of Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series
- 17 Part 14: Industry Standards and Regulations of Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series
- 18 Key Standards and Regulations
- 19 Key Considerations for Industry Standards
- 20 Part 15:Case Studies and Real-World Applications
- 21 Part 16:Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series
- 22 Part 17: The Global Market for Iron Motorcycle Cylinders
- 23
- 24 Part 18: The Future of Iron Motorcycle Cylinders
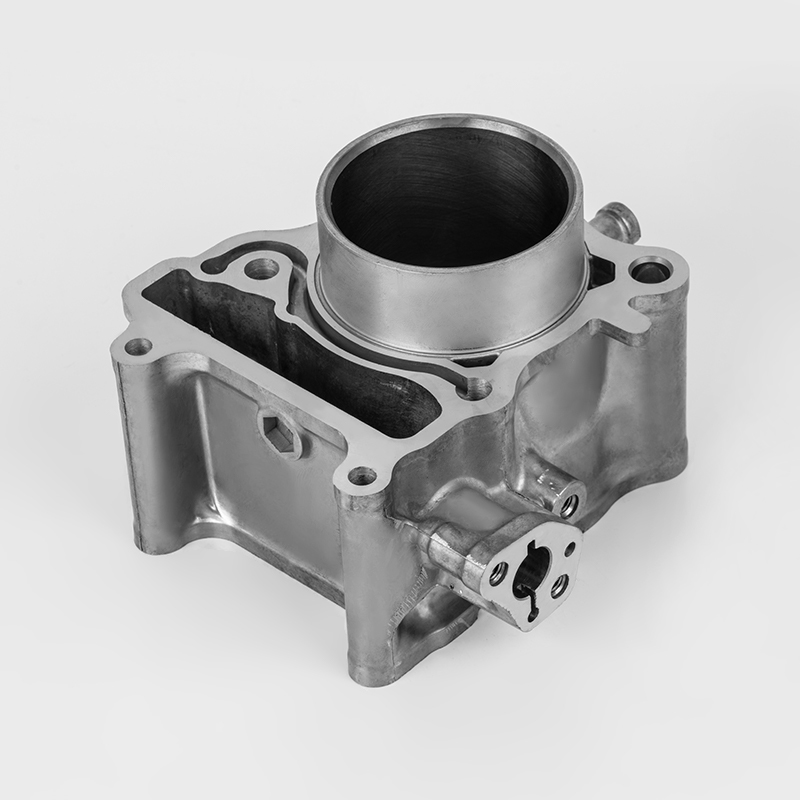
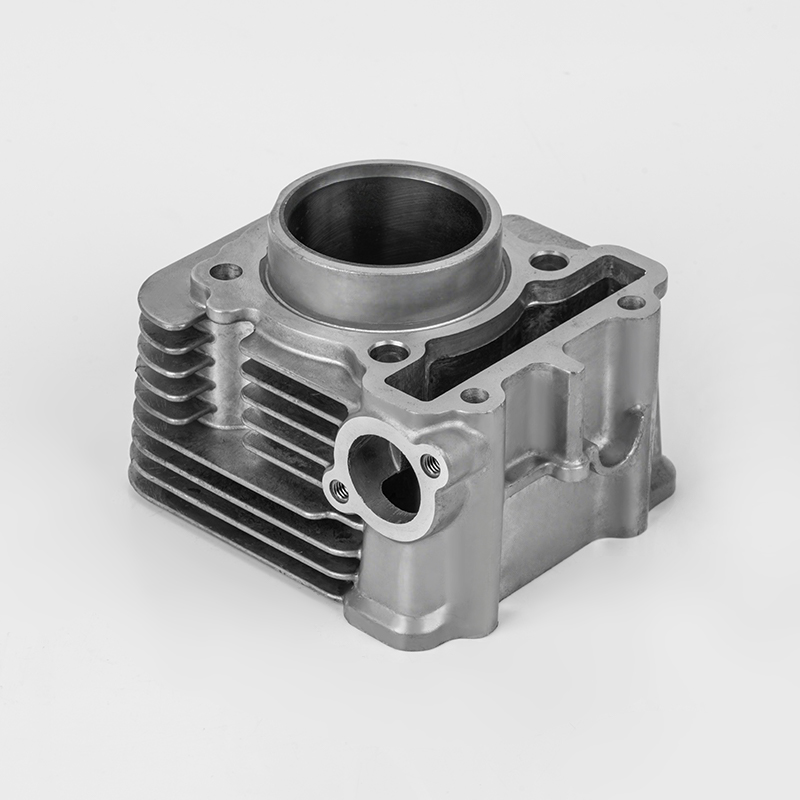
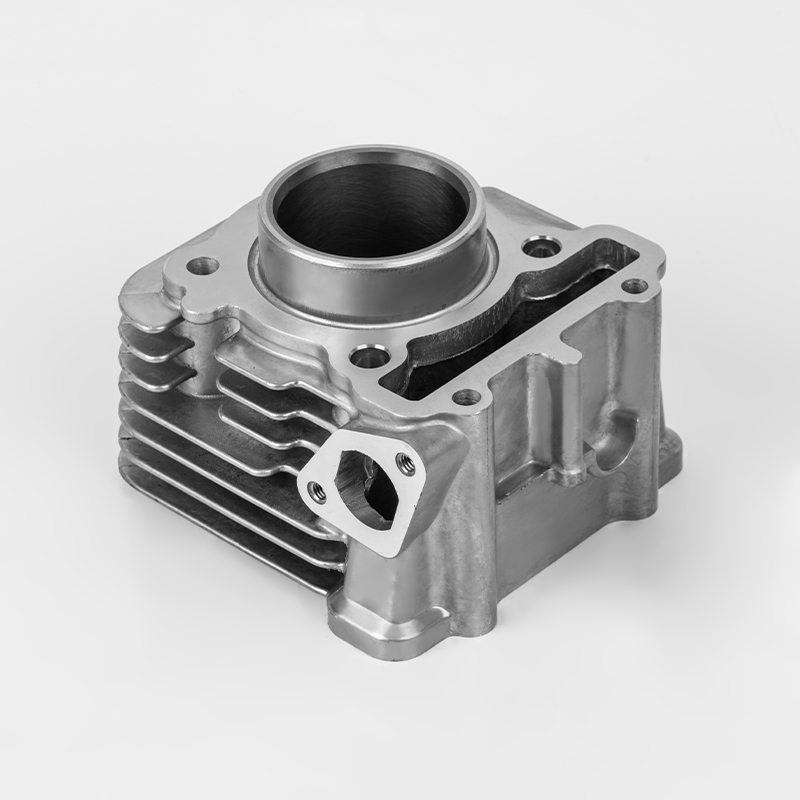
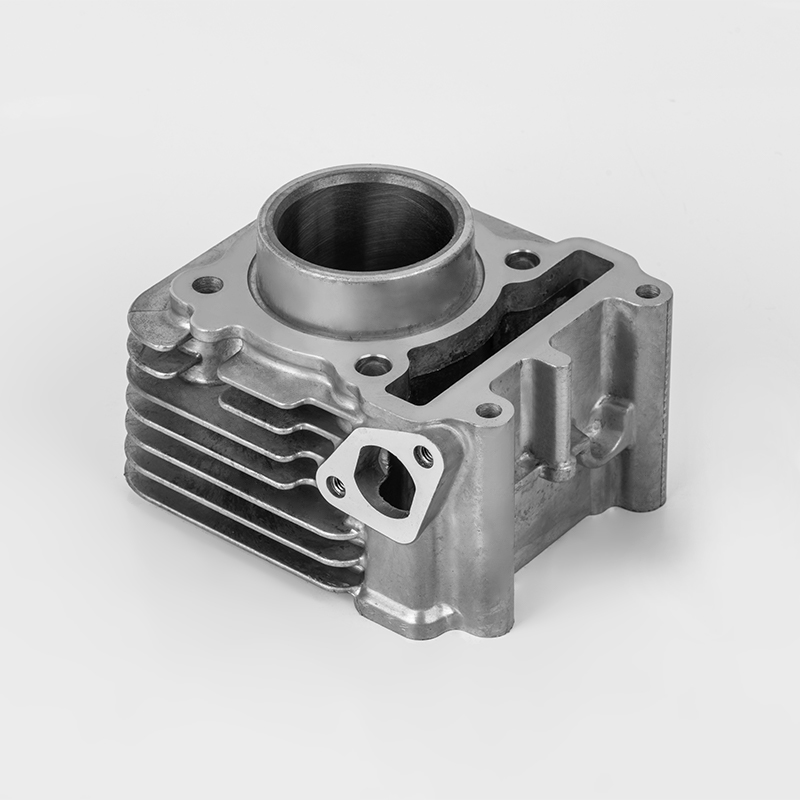
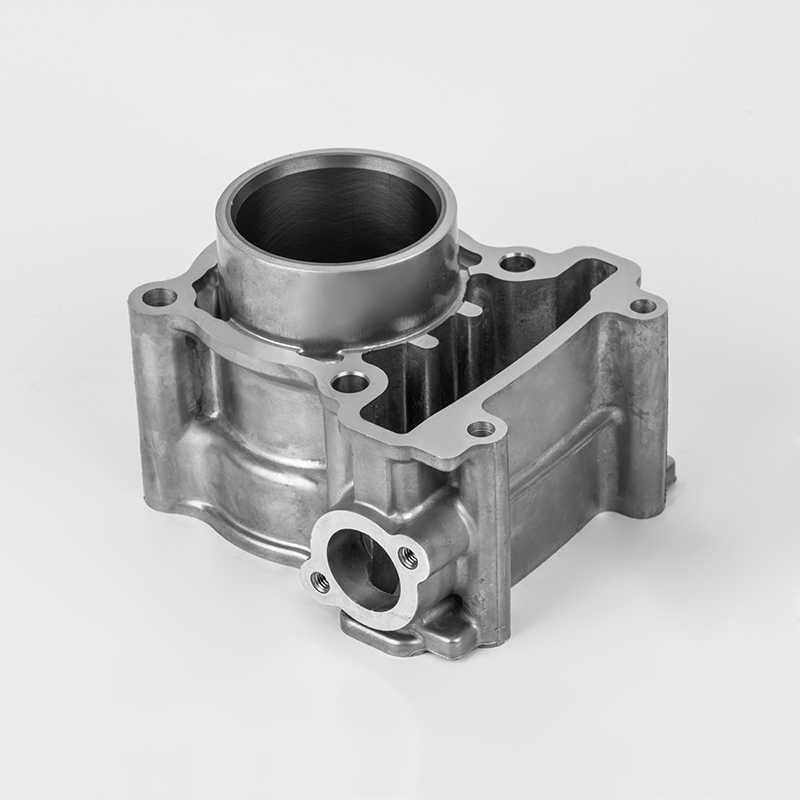
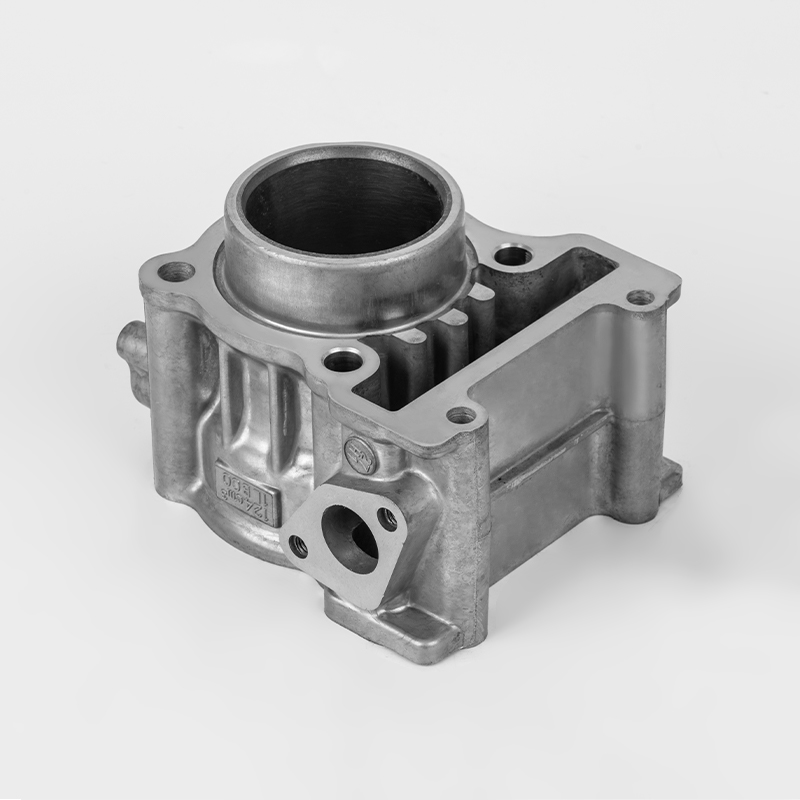
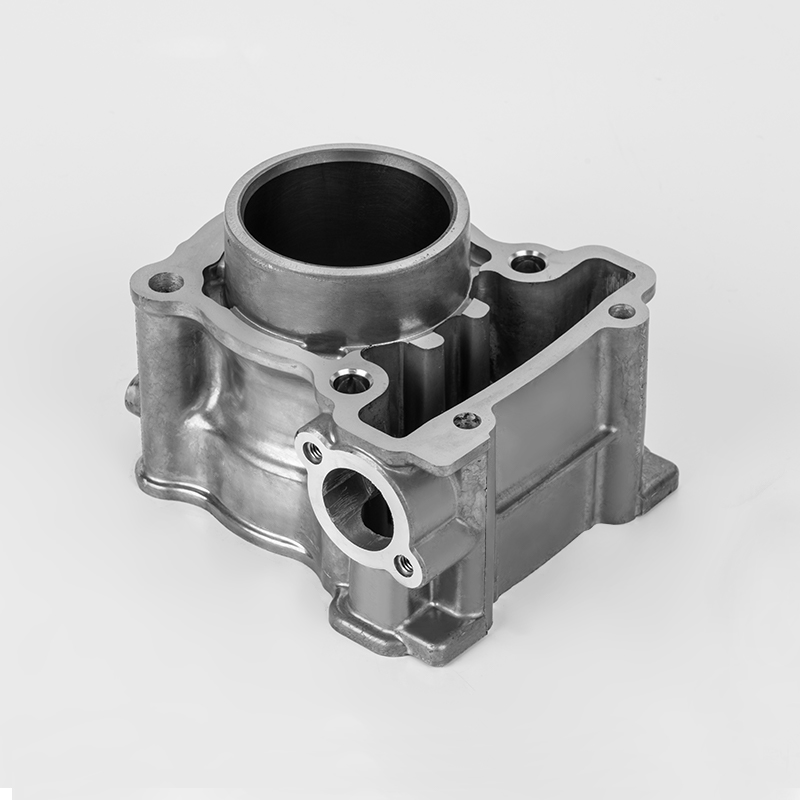
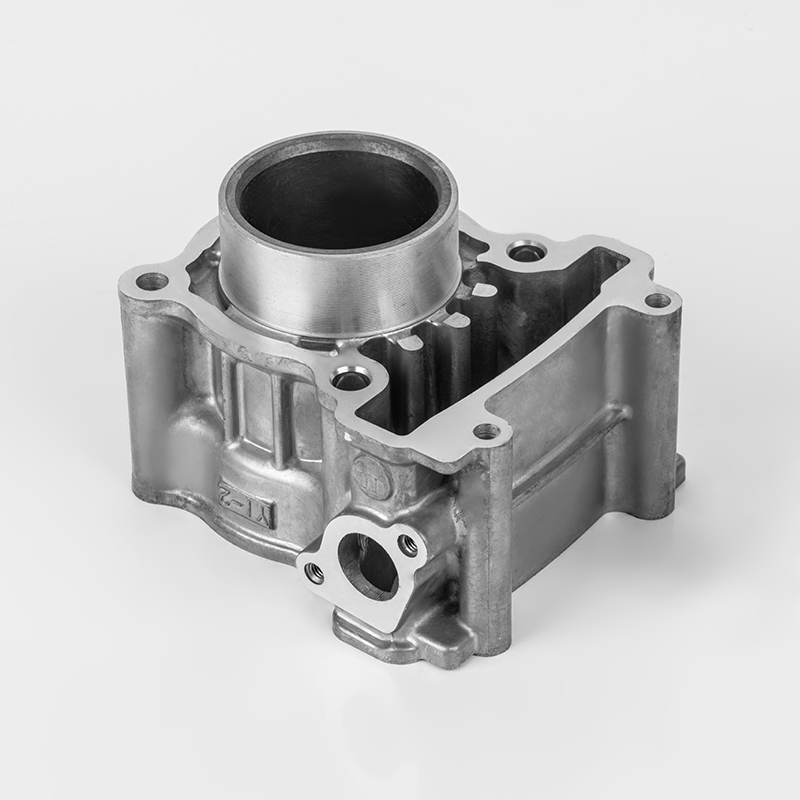
Introduction: What is the Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series?
1. Historical Context and Material Selection
Historically, cast iron has been a preferred material for motorcycle cylinders due to its high compressive strength, thermal stability, and ease of manufacturing. Cast iron cylinders are often used in smaller, lower-powered engines where cost and durability are key factors. However, with the advent of aluminum and other lightweight materials, the use of iron in cylinders has diminished in some applications, though it remains relevant in certain high-torque or heavy-duty applications.
The Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series refers to a range of motorcycle engines and cylinder components made from cast iron, a durable and cost-effective material commonly used in motorcycle manufacturing. These cylinders are known for their robustness, heat resistance, and affordability, making them a popular choice for both budget-conscious riders and enthusiasts.
While the term "Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series" is not a specific brand or model, it generally refers to cylinder parts, engine components, and replacement parts for motorcycles that use cast iron cylinders. These parts are widely used in budget-friendly motorcycles, entry-level bikes, and older models.

Part 1: Understanding the Basics of Motorcycle Cylinders
What is a Cylinder?
A cylinder is a cylindrical chamber within the engine where combustion occurs. In a two-stroke or four-stroke engine, the cylinder is where the fuel-air mixture is ignited, and the piston moves up and down to generate power.
Key Components of a Cylinder:
- Cylinder Block: The main body of the engine.
- Cylinder Head: The top part of the cylinder where the valves and spark plugs are located.
- Piston: Moves within the cylinder to compress the fuel-air mixture.
- Cylinder Liner: A sleeve that guides the piston and ensures proper sealing.
| Component Name | Description |
| Cylinder Block | The main structure of the engine, housing the cylinders and providing support for other components. |
| Cylinder Head | The top part of the cylinder where the valves and spark plugs are located. |
| Piston | A cylindrical component that moves within the cylinder to compress the fuel-air mixture. |
| Cylinder Liner | A sleeve that guides the piston and ensures proper sealing. |
Why Cast Iron?
- Durability: Cast iron is strong and resistant to heat and wear.
- Cost-Effective: Cast iron is inexpensive to produce and easy to machine.
- Heat Resistance: Cast iron can withstand high temperatures without cracking or deforming.
Part 2: The Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series: Buyer’s Guide
Who Buys Iron Motorcycle Cylinders?
- Budget-Conscious Riders: Riders who prioritize low cost and affordability.
- Entry-Level Riders: New riders or those starting with a budget bike.
- Restoration Enthusiasts: Riders who restore classic or vintage motorcycles.
- DIY Mechanics: Riders who perform DIY maintenance and repairs.
What to Look For When Buying
- Compatibility: Ensure the cylinder is compatible with your motorcycle model.
- Quality: Look for high-quality parts from reputable brands.
- Price: Compare prices from different suppliers.
- Warranty: Check for warranty and return policies.
Where to Buy
- Online Marketplaces: Platforms like Alibaba, Amazon, and eBay.
- Specialized Parts Stores: Local motorcycle parts shops.
- Online Forums and Communities: Forums like Reddit, Motorcycle Forums, and Facebook Groups.
Part 3: Common Issues and Solutions of Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series
| Issue | Description | Solution |
| Cracks in Cylinder | Cracks can occur due to thermal stress, poor material quality, or improper repair. | Repair using Flame Powder Spray, brazing, or metal stitching techniques . |
| Bore Polishing | Local areas of the bore surface become polished, leading to increased oil consumption and blow-by. | Improve bore geometry and ensure proper honing techniques to prevent polishing . |
| Worn or Damaged Components | Pistons, rings, or valve stems may wear out, leading to reduced engine performance. | Replace or repair components as per manufacturer specifications . |
| Improper Honing | Poor honing techniques can lead to uneven bore surfaces and reduced engine performance. | Use proper honing techniques, ensure proper oiling, and adjust guide blocks . |
| Material Fatigue | Cast iron can fatigue under repeated stress, leading to cracks or failure. | Use high-quality materials and ensure proper heat treatment and stress relief . |
| Installation Issues | Misalignment or improper installation of cylinder liners can cause performance issues. | Ensure proper alignment and seating of cylinder liners during installation . |
| Corrosion and Contamination | Iron cylinders can suffer from corrosion and contamination from oil or other substances. | Clean and maintain cylinders regularly to prevent corrosion and contamination . |
Part 4: Maintenance Tips of Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series
| Maintenance Tip | Description |
| Proper Break-in Period | New engines should be run with light loads to allow the cylinder surface to handle larger loads gradually, extending the service life of the cylinder surface. |
| Clean Air Intake | Air entering the cylinder should be clean to prevent abrasive wear on the cylinder surface. Using a foam sponge filter can help improve filtration. |
| Lubrication | Proper lubrication is essential to reduce friction and wear. Use lubricating oil with appropriate viscosity for the operating conditions. |
| Avoid Overheating | Overheating can cause engine components to overheat, leading to poor lubrication and cylinder sticking. Regularly clean the heat sink and monitor radiator temperature. |
| Avoid Cold Starts | In cold weather, preheat the engine to ensure proper lubrication before starting. |
| Avoid Carbon Buildup | Carbon deposits can cause cylinder wear. Use special engine oil and clean carbon deposits from the combustion chamber. |
| Regular Maintenance | Follow the manufacturer's scheduled maintenance chart to ensure proper maintenance and timely service. |
| Proper Storage | Store the motorcycle in a stowed position with tires aligned to prevent corrosion and maintain component integrity. |
| Cylinder Honing | Periodically inspect and hone the cylinder to maintain proper dimensions and surface finish. |
| Avoid Engine Knock | Use the correct fuel grade for the engine to prevent engine knock, which can cause cylinder wear. |
Part 5: Manufacturing Methods of Iron Motorcycle Cylinders
| Method | Description | Key Components/Processes | Materials Used | Applications |
| Sand Casting | A traditional method where molten metal is poured into a mold made of sand. | Mold preparation, pouring, cooling, and finishing | Sand, metal (e.g., cast iron) | Engine blocks, cylinder heads |
| Investment Casting | A precision method using a wax pattern that is then coated with a mold material. | Wax pattern, mold material, metal pouring | Wax, metal, mold materials | High-precision parts |
| Die Casting | Molten metal is forced into a mold under high pressure. | Die, mold, metal injection | Metal (e.g., aluminum, steel) | Cylinder barrels, engine components |
| Machining | Precision cutting and shaping of metal parts. | CNC machines, lathes, grinders | Metal (e.g., cast iron, steel) | Cylinder liners, engine components |
| Heat Treatment | Processes to alter the physical and chemical properties of metal. | Heating, quenching, tempering | Metal (e.g., steel) | Cylinder barrels, piston rods |
| Ceramic Bore Liners | Incorporation of ceramic materials into cylinder barrels. | Ceramic liners, ferrous metal sleeves | Ceramic, ferrous metal | Hydraulic cylinders, piston units |
| 3D Printing | Additive manufacturing of metal parts. | 3D printer, metal powder | Metal (e.g., steel, aluminum) | Custom parts, prototypes |
Part 6: Repair Tips of Iron Motorcycle Cylinders
| Repair Method | Description | Key Considerations | Tools/Techniques |
| Flame Powder Spray | A method to repair cracks in cast iron cylinders by applying a coating to improve durability and resistance to wear. | Best for narrow cracks where brazing or welding is not possible. | Requires specialized equipment and expertise. |
| Brazing | A technique to join metal parts by melting and fusing them with a filler metal. | Lower temperature silver or bronze brazing is recommended for proximity to the cylinder to avoid distortion. | Requires brazing rods and appropriate tools. |
| Honing and Boring | Processes to restore or repair worn cylinder bores. | Honing is used to smooth the cylinder bore, while boring is used to enlarge it for oversize pistons. | Requires honing tools, boring bars, and precision equipment. |
| Cylinder Rebuilding | Replacing worn components such as piston rings, valves, or cylinder heads. | May require sending parts to a machine shop for specialized work. | Requires specialized tools and expertise. |
| Lubrication and Cleaning | Proper lubrication and cleaning to prevent wear and ensure smooth operation. | Use appropriate lubricants and keep the cylinder clean to prevent carbon buildup. | Requires regular maintenance and proper lubricants. |
| Compression Testing | A diagnostic method to check for issues like worn piston rings or damaged valves. | Follow manufacturer instructions for accurate results. | Requires a compression tester and proper procedure. |
Part 7: Applications and Use Cases of Iron Motorcycle Cylinders
| Application | Description | Key Features |
| Automotive Industry | Used in engine blocks, cylinder heads, and other engine components. | High strength, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity. |
| Heavy Machinery | Utilized in machinery and equipment components such as machine bases and frames. | Durability and resistance to wear and load conditions. |
| Industrial Equipment | Applied in various industrial equipment like compressors, pneumatic tools, and robotic arms. | Versatility and cost-effectiveness. |
| Transportation | Used in vehicles for components like exhaust manifolds, steering boxes, and gearboxes. | Reliability and durability under high stress. |
| Construction and Heavy Industry | Employed in heavy machinery, cranes, and construction equipment. | Ability to withstand extreme loads and harsh environments. |
| Railway Industry | Used in rail track construction and carriage mechanisms. | Resistance to rust and exposure to extreme weather. |
Part 8: Advantages and Limitations of Iron Motorcycle Cylinders
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
| Durability | Iron cylinders are highly durable and resistant to wear and tear, making them suitable for long-term use. | They can be prone to cracking or warping under extreme stress or high temperatures. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Iron is a cost-effective material, making it accessible for budget-conscious manufacturers and consumers. | The production of iron cylinders can be energy-intensive and may involve high initial costs. |
| Heat Resistance | Iron cylinders can withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for engines that operate under high thermal loads. | Iron has a lower thermal conductivity compared to some other materials, which may affect heat dissipation. |
| Compatibility | Iron cylinders are compatible with a wide range of engine designs and can be used in various motorcycle models. | Compatibility issues may arise when integrating with modern, high-performance engines. |
| Repairability | Iron cylinders are relatively easy to repair and maintain, with common repair methods such as brazing and honing. | Complex repairs may require specialized tools and expertise. |
| Weight | Iron is a relatively heavy material, which can add weight to the motorcycle, potentially affecting performance. | The added weight may reduce fuel efficiency and handling characteristics. |
Part 9: Maintenance Tips of Iron Motorcycle Cylinders
| Maintenance Tip | Description |
| Proper Lubrication | Ensure the cylinder and piston surfaces are well lubricated to reduce friction and wear. |
| Clean Air Intake | Keep the air filter clean to prevent dust and impurities from entering the cylinder and causing abrasive wear. |
| Regular Oil Changes | Change engine oil at recommended intervals to maintain proper lubrication and prevent wear. |
| Avoid Overheating | Prevent engine overheating by maintaining proper cooling and radiator function. |
| Proper Starting and Warm-up | Allow the engine to warm up before operation to ensure proper lubrication and reduce wear. |
| Regular Cleaning | Clean the cylinder and surrounding components to prevent buildup of carbon and other deposits. |
| Correct Installation | Ensure proper installation of cylinder components to avoid misalignment and abnormal wear. |
| Use Quality Lubricants | Use high-quality lubricants and filters to reduce wear and extend component life. |
Part 10: Influencing Factors Longevity of Iron Motorcycle Cylinders
| Factor | Description |
| Material Quality | The quality of the material, such as the carbon content in quenched martensite, significantly affects the mechanical properties and longevity of the cylinder . |
| Maintenance Practices | Regular maintenance, such as oil changes, filter replacements, and proper lubrication, is crucial for extending the life of the cylinder . |
| Operational Conditions | Factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to contaminants can affect the longevity of the cylinder . |
| Load and Stress | High loads and impacts can lead to wear and reduce the lifespan of the cylinder . |
| Environmental Conditions | Extreme temperatures, abrasive dirt, and chemicals can damage the cylinder and reduce its lifespan . |
| Design and Manufacturing | The design and manufacturing quality of the cylinder, including surface treatment and material selection, play a key role in longevity . |
Part 11: Manufacturing Process of Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series
| Process Stage | Description | Key Materials/Techniques |
| Raw Material Preparation | Raw materials such as scrap steel, pig iron, and recycled materials are used. Additional elements like ferrosilicon, ferromanganese, and ferrochromium are added to adjust the composition . | Scrap steel, pig iron, ferrosilicon, ferromanganese, ferrochromium |
| Melting | The raw materials are melted using a medium frequency induction furnace to produce molten iron . | Medium frequency induction furnace |
| Casting | The molten iron is poured into sand molds to form the cylinder block. Sand cores are used to create the water jackets and cylinder chambers . | Sand molds, sand cores |
| Machining | The cast cylinder block undergoes various machining processes, including milling, drilling, and boring to achieve precise dimensions and surface finish . | CNC machines, lathes, boring bars |
| Surface Treatment | Surface treatments such as hardening, chrome plating, or anodizing may be applied to enhance durability and wear resistance . | Hardening, chrome plating, anodizing |
| Quality Control | Inspection and testing are performed to ensure dimensional accuracy, material properties, and surface finish meet specifications . | Dimensional inspection, material testing |
Part 12: Quality Control and Testing of Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series
The Quality Control and Testing of Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series involves a comprehensive set of processes to ensure the durability, reliability, and performance of the cylinders. Several key aspects are highlighted in the provided evidence:
-
- Throughout the manufacturing process, strict quality control measures are implemented to ensure that the cylinders meet strict specifications and tolerances .
- Inspections, measurements, and testing are conducted to verify the integrity and performance of the finished cylinders .
- Material inspection, dimensional checks, and material analysis are used to ensure the quality of the materials and components .
-
- Various testing procedures are employed to ensure the cylinders meet the required standards. These include mechanical tests (e.g., yield strength, tensile strength, bend test), chemical analysis, and visual inspections .
- Pressure testing, leak testing, and durability testing are used to ensure the cylinders can withstand operational stresses .
- Advanced tools such as Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) and X-ray testing are used to ensure precision and quality .
-
- The use of high-quality materials and precision manufacturing processes is crucial for the production of durable and reliable cylinders .
- The manufacturing process involves casting, machining, and surface treatments to enhance the performance and longevity of the cylinders .
-
- Quality assurance is reflected through ISO certifications and adherence to international standards .
- Quality control measures help in identifying and rectifying defects early in the production process, ensuring the final product meets the required standards .
Part 13: Performance Characteristics and Performance Metrics of Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series
| Characteristic | Description |
| Durability | Iron cylinders are known for their durability and resistance to wear and tear, making them suitable for long-term use . |
| Heat Resistance | Iron cylinders can withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for engines that operate under high thermal loads . |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Iron is a cost-effective material, making it accessible for budget-conscious manufacturers and consumers . |
| Material Quality | The use of high-quality materials and surface treatments enhances the durability and wear resistance of the cylinders . |
| Performance Metrics | Common performance metrics include speed, acceleration, braking, fuel consumption, emissions, noise, vibration, and handling . |
| Testing and Quality Control | Quality control measures, including inspections, measurements, and testing, ensure the cylinders meet strict specifications and tolerances . |
| Manufacturing Process | The manufacturing process involves casting, machining, and surface treatments to enhance the performance and longevity of the cylinders . |
Part 14: Industry Standards and Regulations of Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series
The industry standards and regulations for iron motorcycle cylinders are primarily governed by a combination of international and national standards organizations, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and national bodies like the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). These standards ensure the quality, safety, and performance of cylinders used in various applications, including motorcycles, industrial equipment, and industrial cylinders.
Key Standards and Regulations
-
- ISO 11439: This standard is an International Standard for CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) cylinders, applicable to on-board cylinders. It is widely adopted by countries like Malaysia, Iran, Thailand, and Egypt .
- ISO 4705D and ISO 9809: These standards are for industrial cylinders, ensuring safety and uniformity in design and manufacturing .
- ISO 15552 and VDMA 24562: These standards are used for pneumatic and hydraulic cylinders, ensuring interchangeability and compatibility of components .
- ISO 8133, ISO 6547, ISO 3320, ISO 3322, ISO 4393, ISO 4395: These standards cover dimensions, tolerances, and mounting specifications for various types of cylinders .
-
- Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS): India follows ISO standards for cylinder manufacturing, with ISO 11439, ISO 4705D, and ISO 9809 being key standards for industrial and CNG cylinders .
- ASTM International: Standards like A667/A667M-87 cover centrifugally cast dual-metal cylinders (gray and white iron) for pressure-containing applications .
-
- ASTM A48/A48M-22: Specifies gray iron castings for pressure-containing parts .
- ASTM A667/A667M-87: Specifies centrifugally cast dual-metal cylinders for pressure-containing applications .
- BS 5755, BS 6331, BS 5755 (ISO 4393), BS 6331 (ISO 6099): These British standards cover stroke lengths, mounting styles, and piston rod threads for cylinders .
-
- NFPA (National Fire Protection Association): Standards for industrial air cylinders and safety requirements .
- VDMA 24562: A European standard for pneumatic cylinders, ensuring interchangeability and compatibility .
Key Considerations for Industry Standards
- Quality Control and Testing: Rigorous quality control measures are implemented to ensure dimensional accuracy, material integrity, and performance of cylinders .
- Safety and Compliance: Standards ensure safety, reliability, and compliance with international and national regulations .
- Interchangeability and Compatibility: Standards like ISO 15552 and VDMA 24562 ensure component interchangeability and compatibility across different manufacturers .
Part 15:Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Case Study 1: Restoration of a Vintage Motorcycle Cylinder
A vintage motorcycle enthusiast had a cast iron cylinder that suffered from a deep crack. The repair involved:
- Flame Powder Spray to fill the crack.
- Brazing to bond the repair.
- Metal Stitching to reinforce the area.
The result was a fully restored cylinder that restored the motorcycle’s original performance.
Case Study 2: Industrial Application in Heavy Machinery
In a heavy-duty industrial setting, an iron cylinder was used in a high-torque engine. The cylinder was subjected to:
- High temperatures and pressures.
- Regular maintenance to prevent thermal stress and cracking.
- Long-term durability due to the strength of the iron material.
Part 16:Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Iron Motorcycle Cylinder Series
| Aspect | Description |
| Material and Manufacturing | Iron is a recyclable material, which reduces the demand for new raw materials and minimizes environmental impact . |
| Environmental Impact | The manufacturing process involves stages like melting, casting, and machining, which can generate pollutants such as particulate matter and VOCs. However, strict quality control measures are implemented to ensure compliance with environmental standards . |
| Sustainability Initiatives | Life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies, such as ISO 14040 and ISO 14044, help evaluate and improve the environmental performance of products . |
| Energy and Resource Use | The use of recycled materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes helps reduce the environmental footprint of iron production . |
| End-of-Life Management | Recycling and proper disposal of iron cylinders contribute to resource conservation and reduced environmental impact . |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to international and national standards (e.g., ISO standards) ensures quality, safety, and environmental compliance . |
Part 17: The Global Market for Iron Motorcycle Cylinders
Market Overview
The global market for iron motorcycle cylinders is a fragmented and niche market, primarily driven by budget-conscious consumers, restoration enthusiasts, and DIY mechanics. While the high-performance and luxury motorcycle market has shifted towards aluminum and composite materials, the iron cylinder market remains a steady niche segment.
Key Market Players
- Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs): Companies like Honda, Yamaha, Suzuki, and Kawasaki produce iron cylinders for their budget and entry-level models.
- Aftermarket Suppliers: Companies like Alibaba, Amazon, and specialized parts retailers supply replacement and remanufactured cylinders.
- Restoration and Classic Bike Shops: Businesses specializing in classic and vintage motorcycle restoration.
Market Trends
- Declining Demand for Iron Cylinders in High-End Models: As high-performance motorcycles increasingly use aluminum and composite cylinders, the demand for iron cylinders in this segment is decreasing.
- Steady Demand in Budget and Entry-Level Models: Iron cylinders continue to be popular in budget and entry-level motorcycles, especially in emerging markets.
- Growth in Restoration and Classic Bike Markets: The restoration and classic bike market provides a steady demand for iron cylinders, especially for original and remanufactured parts.
Part 18: The Future of Iron Motorcycle Cylinders
Trends in Motorcycle Engine Technology
- Shift to Aluminum: Many modern motorcycles use aluminum cylinders for lightweight and high-performance.
- Hybrid and Electric Motors: The rise of electric motorcycles may reduce the need for traditional cylinders.
- Advancements in Materials: New materials like composite materials and ceramics may replace cast iron in the future.
The Role of Iron Cylinders
- Affordability and Durability: Iron cylinders will continue to be popular in budget and entry-level bikes.
- Niche Market: They will remain relevant in restoration and classic bike markets.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى