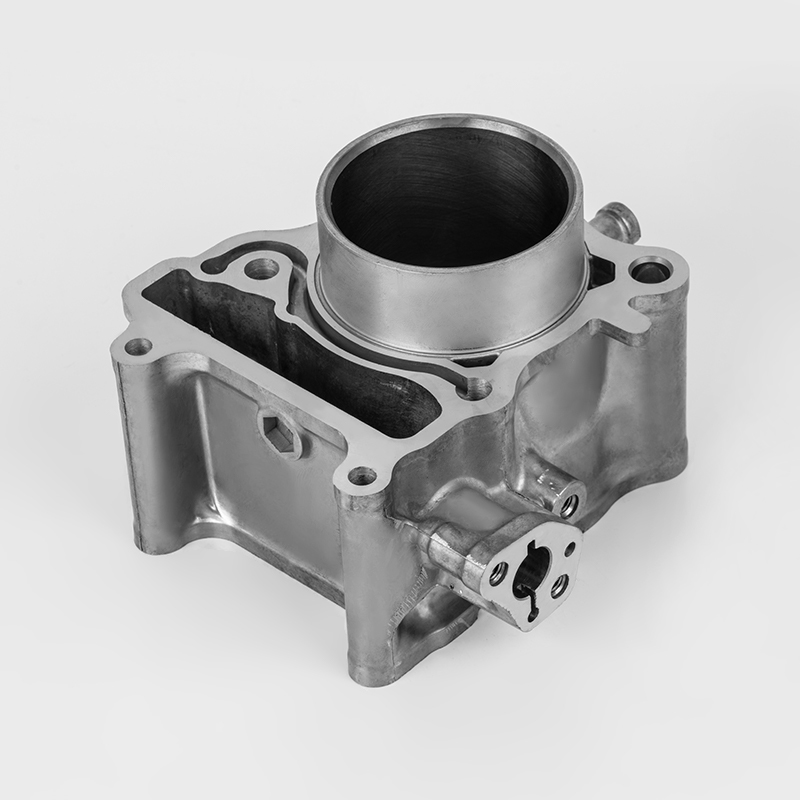
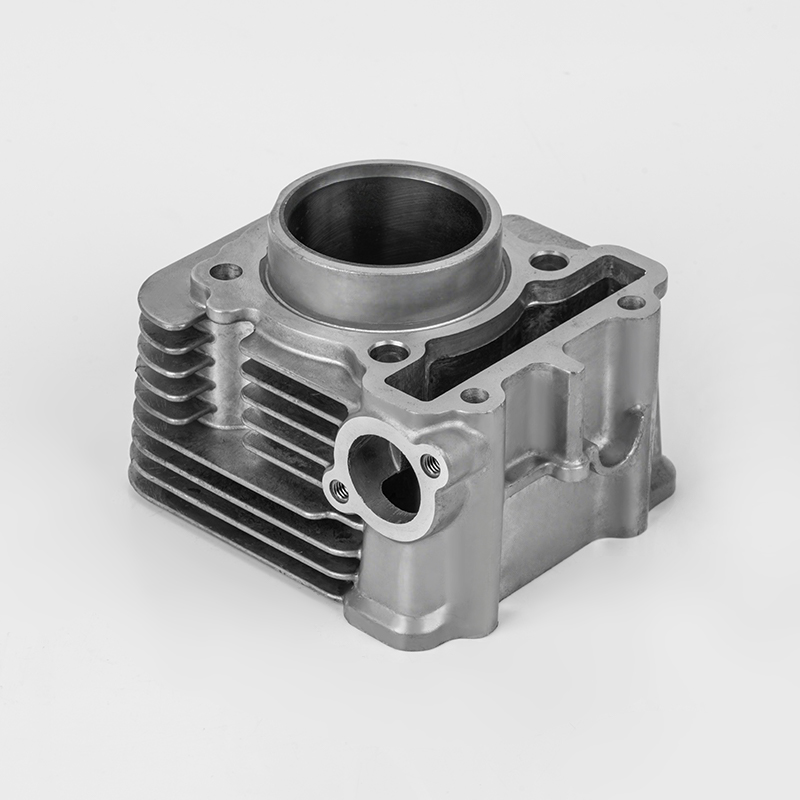
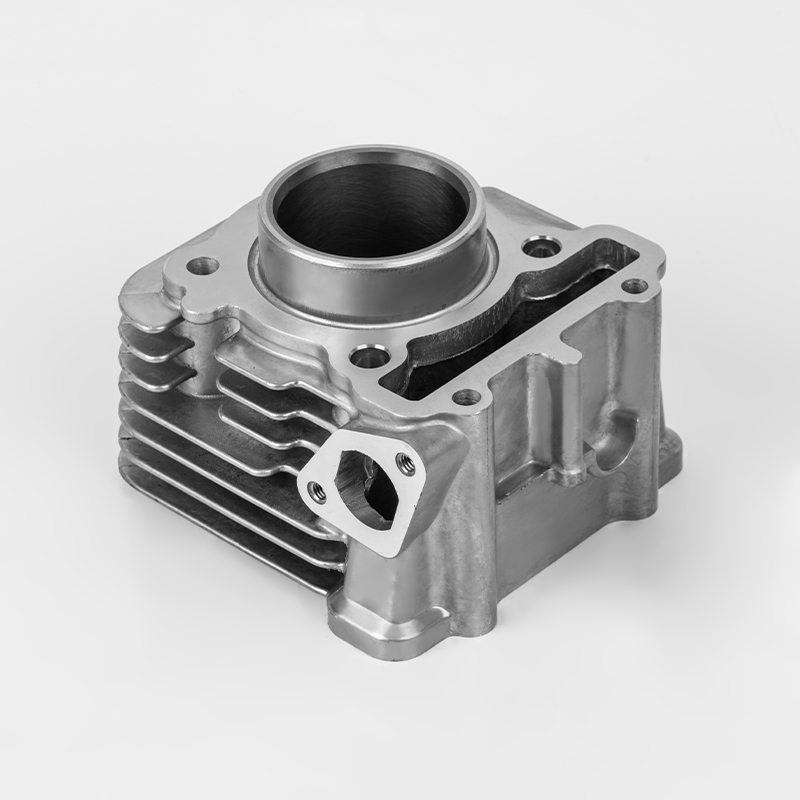
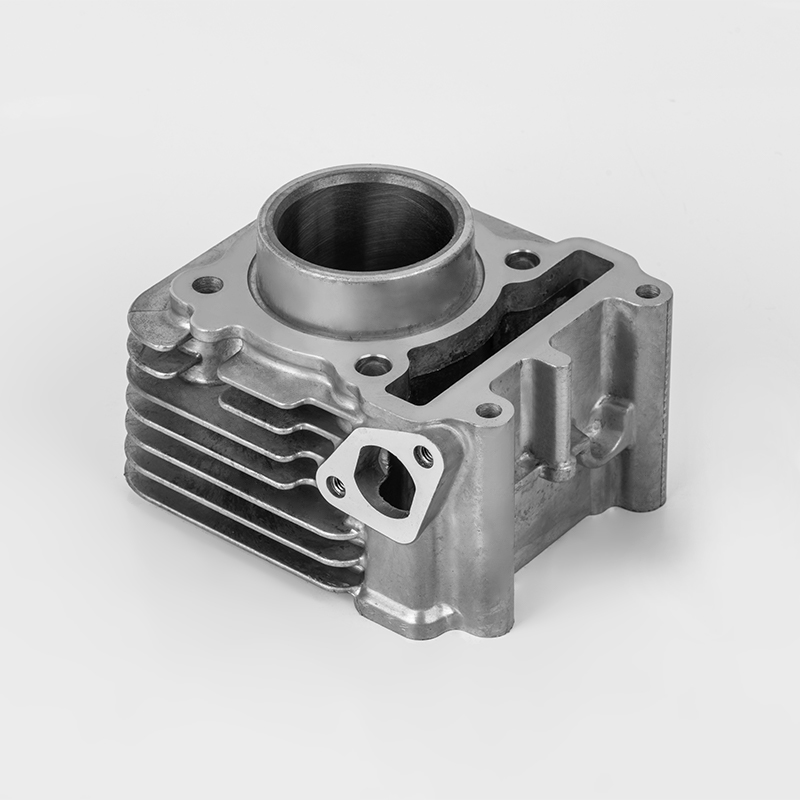
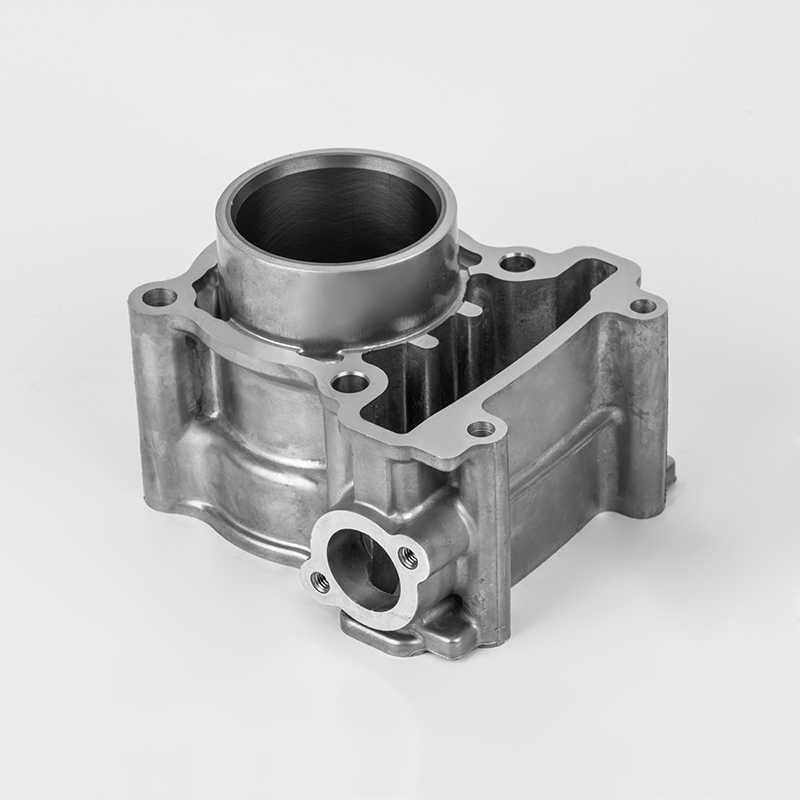
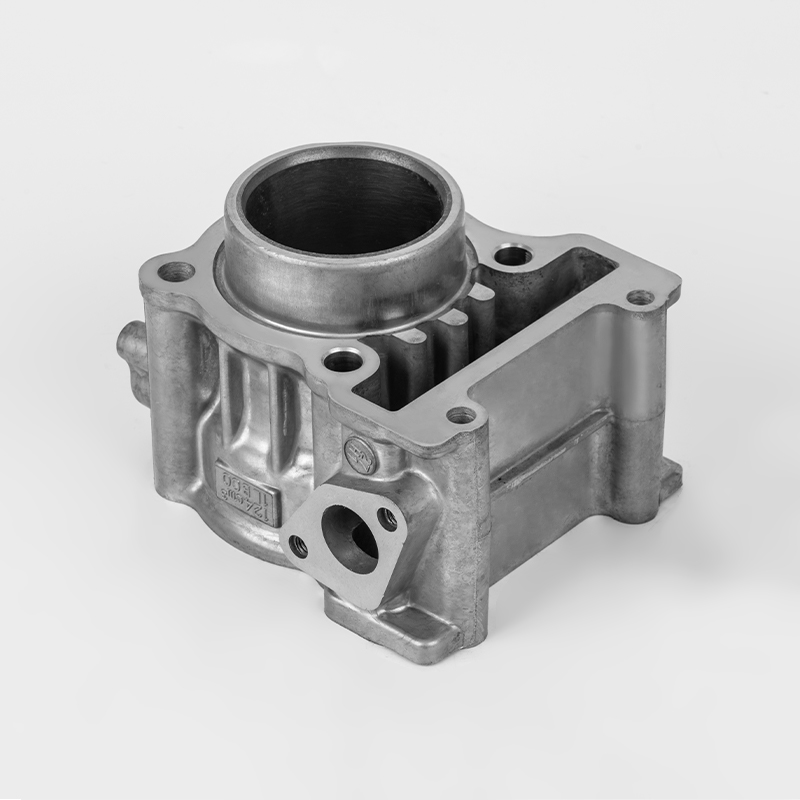
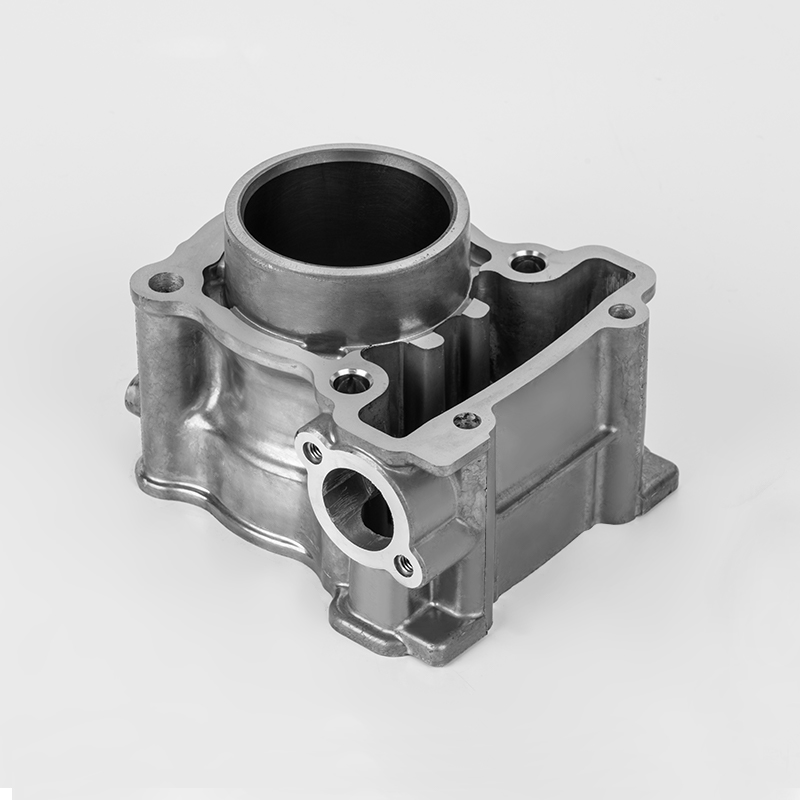
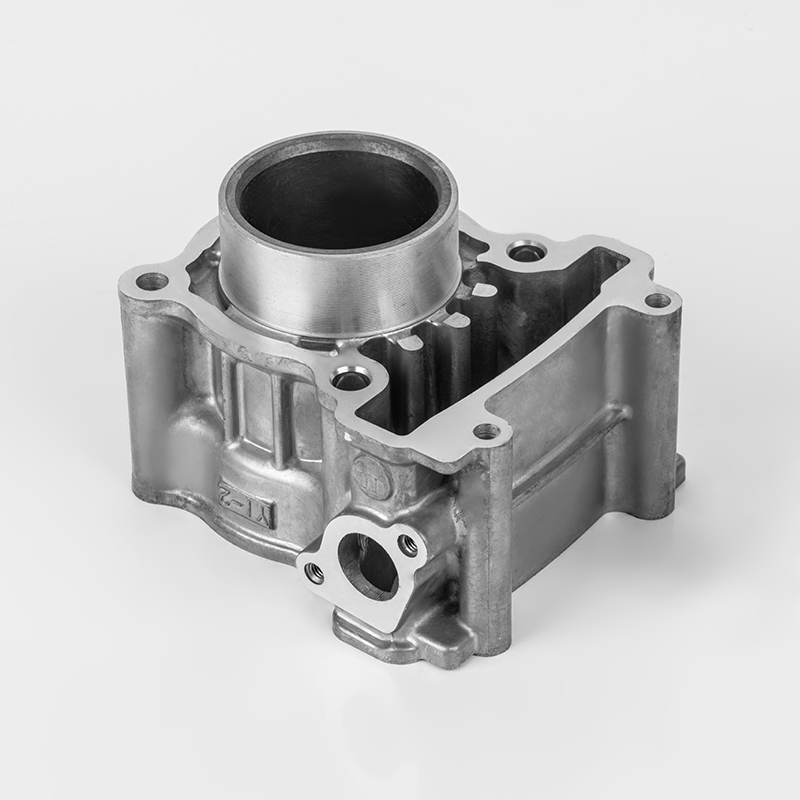
Motorcycle cylinders are a critical component of motorcycle engines, responsible for converting fuel into mechanical energy. Understanding the various aspects of motorcycle cylinders, including their types, maintenance, and market dynamics, is essential for buyers and enthusiasts. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of motorcycle cylinders, covering their functions, types, maintenance, and market trends.

Content
- 1 1. What is a Motorcycle Cylinder?
- 2 2. Types of Motorcycle Cylinders
- 3 3. How Motorcycle Cylinders Work
- 4 4. Functions of the Motorcycle Cylinder
- 5 5. Maintenance of Motorcycle Cylinders
- 6 6. Construction of Motorcycle Cylinders
- 7 7. Materials of Motorcycle Cylinders
- 8 8. Common Issues and Troubleshooting of Motorcycle Cylinders
- 9 8. Purchasing Tips for Motorcycle Cylinders
- 10 8. Motorcycle Cylinder Market and Buyers
- 11 9. Installation Tips of Motorcycle Cylinders
- 12 10. Market and Consumer Behavior
- 13 11. Environmental and Economic Considerations
- 14 12. The Evolution of Motorcycle Cylinders
- 15 13. Challenges and Opportunities in the Industry
- 16 14. The Role of Aftermarket Parts in the Motorcycle Cylinder Market
- 17 15. The Role of Cylinder in Motorcycle Performance and Efficiency
- 18 16. The Impact of Cylinder on Fuel Efficiency and Emissions
- 19 17. The Role of Cylinder in Motorcycle Safety
- 20 18. The Role of Cylinder in Motorcycle Customization and Racing
- 21 19. The Role of Cylinder in Motorcycle Maintenance and Longevity
- 22 20. The Enduring Importance of Motorcycle Cylinders
- 23 21. The Role of Cylinder Design in Engine Performance
- 24 22. The Future of Motorcycle Cylinder Technology
1. What is a Motorcycle Cylinder?
A motorcycle cylinder is a cylindrical chamber within the engine that houses the piston and is responsible for the combustion process. The cylinder is a key component of the engine's power generation system. The combustion of fuel within the cylinder generates the force that drives the motorcycle's movement.
1.1. Cylinder Types
- Single-Cylinder Engines: These are the most basic type of motorcycle engines, known for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. They are commonly used in smaller motorcycles and scooters.
- Multi-Cylinder Engines: These engines use multiple cylinders to generate more power and provide smoother operation. Common configurations include twin-cylinder, triple-cylinder, and four-cylinder engines.
- Cylinder Layouts: Cylinders can be arranged in various configurations, such as inline, V-type, or opposed cylinders, depending on the motorcycle's design and performance requirements.
1.2. Cylinder Materials
- Aluminum-Cylinder (DiASil): Yamaha's DiASil cylinder is an all-aluminum cylinder design that eliminates the need for a steel cylinder sleeve, offering better heat dissipation and reduced weight.
- Steel-Cylinder: Traditional steel cylinders are still used in some motorcycles, especially in budget-friendly models.
1.3. Cylinder Function
The cylinder is responsible for the combustion process, where fuel and air are mixed and ignited to produce power. The piston moves within the cylinder, converting the force from combustion into mechanical energy.
1.4. Cylinder Components
- Cylinder Block: The main structure that houses the cylinders and supports the engine components.
- Piston: Moves within the cylinder to convert combustion energy into mechanical motion.
- Cylinder Head: Contains the valves and spark plugs.
- Connecting Rod: Connects the piston to the crankshaft.
- Crankshaft: Converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion .
2. Types of Motorcycle Cylinders
| Cylinder Type | Description | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
| Single-Cylinder | One cylinder with a single piston. | Simple, reliable, lightweight, good for low-speed riding. | Entry-level motorcycles, off-road bikes, dirt bikes. |
| Boxer Engine | Two horizontally opposed cylinders. | Low center of gravity, smooth operation, unique appearance. | Touring and adventure bikes. |
| Parallel-Twin | Two cylinders in a straight line. | Common in many motorcycles, good balance and power. | Various motorcycle models, including cruisers and sportbikes. |
| V-Twin | Two cylinders arranged in a V-shape. | High power, smooth operation, often used in high-performance bikes. | Sportbikes, cruisers, and touring motorcycles. |
| Inline-Triple | Three cylinders in a straight line. | Smooth operation, good power delivery. | Sportbikes and some cruisers. |
| V4 | Four cylinders in a V-shape. | High power, smooth operation, often used in sportbikes. | High-performance motorcycles. |
| Inline-Four | Four cylinders in a straight line. | Smooth operation, good power, common in larger motorcycles. | Touring and sportbikes. |
| Flat-Boxer | Two horizontally opposed cylinders. | Low center of gravity, smooth operation. | Some high-performance and custom motorcycles. |
| Wankel Engine | Rotary engine with a single rotor. | Compact, smooth operation, high RPM capability. | Limited use in some high-performance motorcycles. |
3. How Motorcycle Cylinders Work
4. Functions of the Motorcycle Cylinder
| Function | Description | Key Characteristics |
| Combustion Chamber | The cylinder serves as the combustion chamber where fuel and air are mixed and ignited to produce power. | The cylinder must be sealed to maintain the combustion process. |
| Piston Movement | The cylinder provides a sealed space for the piston to move, converting the energy from combustion into mechanical motion. | The cylinder must be strong enough to withstand high temperatures and pressures. |
| Guidance for Piston | The cylinder guides the piston during its movement, ensuring smooth and efficient operation. | The cylinder must maintain precise roundness and cylindricity to reduce wear and tear. |
| Heat Dissipation | The cylinder is designed to dissipate heat generated during combustion. | Materials like cast iron or aluminum are used to enhance heat dissipation. |
| Structural Integrity | The cylinder forms the core structure of the engine, supporting other components like the crankshaft and connecting rods. | The cylinder must be durable to withstand high pressures and temperatures. |
| Cooling | In multi-cylinder engines, the cylinder is often part of a cooling system (e.g., water jackets) to maintain optimal operating temperatures. | Air-cooled or liquid-cooled systems are used depending on the engine design. |
5. Maintenance of Motorcycle Cylinders
| Maintenance Aspect | Description | Importance |
| Regular Cleaning | Keeping the cylinder and surrounding areas clean to prevent dust and debris from entering the combustion chamber. | Prevents wear and tear and ensures efficient combustion. |
| Lubrication | Applying the correct type of lubricating oil to the cylinder and piston surfaces to reduce friction and wear. | Essential for reducing friction and extending the life of the cylinder. |
| Cooling System Maintenance | Ensuring the cooling system is functioning properly to maintain optimal operating temperatures. | Prevents overheating and ensures the engine operates efficiently. |
| Regular Inspections | Regularly inspecting the cylinder for signs of wear, cracks, or damage. | Helps identify issues early and prevent more serious problems. |
| Proper Fuel Quality | Using high-quality fuel and additives to prevent carbon buildup and ensure efficient combustion. | Improves engine performance and reduces the risk of engine damage. |
| Avoiding Overheating | Monitoring and controlling engine temperature to prevent overheating. | Prevents damage to the cylinder and other engine components. |
| Proper Storage | Storing the motorcycle in a clean and dry environment to prevent corrosion and damage. | Protects the cylinder and other components from environmental damage. |
6. Construction of Motorcycle Cylinders
| Component | Description | Material/Process | Purpose |
| Cylinder Block | The main structure that houses the cylinders and supports the engine components. | Cast iron or aluminum alloy. | Provides structural integrity and support for the engine. |
| Cylinder Liner | A cylindrical sleeve that is pressed into the cylinder block. | Cast iron or aluminum alloy. | Provides a surface for the piston to move and withstand combustion pressures. |
| Piston | Moves within the cylinder to convert combustion energy into mechanical motion. | Aluminum alloy. | Converts thermal energy into mechanical motion. |
| Piston Rings | Seals the gap between the piston and the cylinder wall. | Carbon steel or cast iron. | Ensures proper sealing and lubrication. |
| Cylinder Head | Covers the top of the cylinder and contains the valves and spark plugs. | Aluminum alloy. | Provides access to the combustion chamber and supports the valves. |
| Connecting Rod | Connects the piston to the crankshaft. | Carbon steel. | Transfers the linear motion of the piston to the crankshaft. |
| Crankshaft | Converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion. | Carbon steel. | The primary source of power transmission. |
| Valves | Control the flow of air-fuel mixture into and out of the cylinder. | Carbon steel. | Regulate the intake and exhaust of gases. |
| Spark Plug | Ignites the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber. | Ceramic and metal. | Initiates the combustion process. |
| Cooling System | Manages the heat generated during combustion. | Aluminum, copper, or plastic. | Prevents overheating and ensures optimal engine temperature. |
| Lubrication System | Reduces friction and wear between moving parts. | Engine oil. | Ensures smooth operation and extends component life. |
7. Materials of Motorcycle Cylinders
Motorcycle cylinders are constructed using a variety of materials, each chosen for their specific properties to ensure durability, performance, and efficiency. The materials used in motorcycle cylinders include:
The choice of materials depends on the specific application and performance requirements of the engine. For example, high-performance engines may use aluminum alloys for pistons and cylinder heads to reduce weight and improve thermal efficiency .
8. Common Issues and Troubleshooting of Motorcycle Cylinders
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
| Cylinder Leakage | Damaged cylinder head gasket, worn cylinder liner, or loose cylinder head bolts | Replace or repair the damaged gasket or liner, tighten the cylinder head bolts properly. |
| Loss of Compression | Worn piston rings, damaged cylinder walls, or valve issues | Replace worn components, inspect and repair the cylinder and valves. |
| Cylinder Overheating | Inadequate cooling, clogged cooling system, or engine overloading | Clean the cooling system, ensure proper airflow, and avoid overloading the engine. |
| Cylinder Wear | High mileage, poor maintenance, or incorrect engine operation | Inspect and replace worn components, follow proper maintenance procedures. |
| Cylinder Misalignment | Uneven tightening of cylinder head bolts, or distorted cylinder block | Retighten the cylinder head bolts evenly, inspect and repair the cylinder block if necessary. |
| Cylinder Drift | Internal leaks or pressure issues in the hydraulic system (if applicable) | Adjust system pressure, inspect and repair internal components. |
| Cylinder Noise | Worn bearings, loose components, or internal damage | Inspect and replace worn components, check for internal damage. |
8. Purchasing Tips for Motorcycle Cylinders
| Tip | Description |
| Verify Compatibility | Ensure the cylinder is compatible with your motorcycle model and engine type. |
| Check Material Quality | Choose cylinders made from durable and corrosion-resistant materials. |
| Inspect for Wear and Damage | Look for signs of wear, cracks, or damage before purchasing. |
| Consult Reputable Suppliers | Purchase from trusted suppliers to ensure quality and authenticity. |
| Consider Maintenance Needs | Choose cylinders that are easy to maintain and have good longevity. |
| Check for Accessories | Ensure the cylinder comes with necessary accessories for proper installation. |
| Verify OEM vs. Aftermarket | Decide whether to use OEM or aftermarket parts based on your needs. |
| Read Reviews and Testimonials | Look for user reviews and expert opinions on the product. |
8. Motorcycle Cylinder Market and Buyers
The motorcycle cylinder market is a significant segment of the automotive industry, with a wide range of products available for various motorcycle models and budgets.
8.1. Types of Motorcycle Cylinders
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) Parts: These are cylinders produced by the motorcycle manufacturer and are designed to meet the original specifications.
- Aftermarket Parts: These are cylinders produced by third-party manufacturers and are often more affordable than OEM parts.
- Custom and Modified Cylinders: These are designed for specific performance or aesthetic purposes, often used in racing or custom motorcycles.
8.2. Suppliers and Retailers
- Online Marketplaces: Platforms like Alibaba.com and Made-in-China.com offer a wide range of motorcycle cylinder parts, with options for customization and bulk orders.
- Specialized Retailers: Many motorcycle shops and online retailers offer a variety of cylinder parts, often with expert advice and support.
8.3. Buyer Considerations
- Compatibility: Ensure that the cylinder is compatible with your motorcycle model and engine type.
- Quality and Durability: Choose high-quality parts from reputable manufacturers to ensure longevity and reliability.
- Warranty and Support: Look for products with warranty and support options to ensure peace of mind.
9. Installation Tips of Motorcycle Cylinders
| Installation Step | Description |
| Prepare the Cylinder and Piston | Ensure the cylinder and piston are clean and free from debris. |
| Install Piston Rings | Properly install the piston rings with correct end gaps and markings facing up. |
| Position the Cylinder | Align the cylinder with the crankcase and dowel pins to ensure proper alignment. |
| Install Cylinder Gasket | Ensure the cylinder gasket is properly positioned and free from debris. |
| Torque Cylinder Bolts | Tighten the cylinder bolts in a crisscross pattern to the manufacturer's specifications. |
| Check for Proper Seating | Ensure the cylinder is properly seated and there are no obstructions. |
| Test Engine Operation | Start the engine and check for any issues such as leaks or unusual noises. |
10. Market and Consumer Behavior
Consumer buying behavior for motorcycle cylinders is influenced by factors such as price, brand, quality, and safety. Buyers often look for reliable, durable, and cost-effective products. Online platforms and specialized retailers offer a wide range of options for consumers.
Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
- Price: Consumers are often sensitive to price, especially for high-end motorcycles.
- Brand: Brand reputation and reliability are important factors in consumer decisions.
- Quality: Consumers look for high-quality products that offer good performance and durability.
- Safety: Safety features and reliability are important considerations for many buyers.
Online Platforms and Retailers
Online platforms such as Amazon, eBay, and specialized motorcycle retailers offer a wide range of motorcycle cylinders and engine components. These platforms provide detailed product information, user reviews, and expert advice.
11. Environmental and Economic Considerations
11.1. Environmental Impact
The production and use of motorcycle cylinders have environmental implications. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on reducing emissions and improving fuel efficiency. Advances in materials and manufacturing processes are helping to reduce the environmental footprint of motorcycle engines.
11.2. Economic Factors
The motorcycle cylinder market is influenced by economic factors such as fuel prices, consumer demand, and technological advancements. Economic downturns can affect the demand for motorcycles and related parts, while economic growth can drive innovation and market expansion.
12. The Evolution of Motorcycle Cylinders
The history of motorcycle cylinders is a fascinating journey of innovation, from the early days of internal combustion engines to the advanced designs of today. Understanding the evolution of motorcycle cylinders provides valuable insight into the development of motorcycle technology and the broader automotive industry.
Early Developments
The first motorcycle engines were simple and rudimentary. Early engines were often single-cylinder, with basic designs that prioritized simplicity and reliability. These early engines were typically air-cooled and had limited power output. The development of the four-stroke cycle in the late 19th century marked a significant advancement in engine design.
The Rise of Multi-Cylinder Engines
As motorcycle technology advanced, the need for more power and smoother operation led to the development of multi-cylinder engines. The introduction of two-cylinder engines in the early 20th century provided a more balanced and powerful alternative to single-cylinder designs. The development of V-twin engines in the mid-20th century further improved engine smoothness and performance.
Modern Innovations
In recent decades, advancements in materials science, manufacturing techniques, and engine design have led to significant improvements in motorcycle cylinder technology. The introduction of aluminum cylinder blocks, improved cooling systems, and advanced combustion technologies have enhanced engine performance and durability.
13. Challenges and Opportunities in the Industry
The motorcycle cylinder industry faces several challenges, including intense competition, regulatory pressures, and the need for continuous innovation. However, there are also significant opportunities for growth and development.
Challenges
- Competition: The market is highly competitive, with numerous players vying for market share.
- Regulatory Compliance: Strict environmental regulations and safety standards require significant investment in compliance.
- Technological Obsolescence: Rapid technological advancements can lead to obsolescence of existing products.
Opportunities
- Emerging Markets: Growing demand in emerging markets presents significant growth opportunities.
- Innovation: Continuous innovation in materials and design can lead to new product developments.
- Sustainability: Focus on sustainability and eco-friendly solutions can drive new market opportunities.
14. The Role of Aftermarket Parts in the Motorcycle Cylinder Market
The aftermarket parts market for motorcycle cylinders is a significant segment of the overall motorcycle industry. Aftermarket parts are produced by third-party manufacturers and are sold to consumers who are not the original equipment manufacturers.
14.1. Advantages of Aftermarket Parts
- Cost-Effectiveness: Aftermarket parts are often more affordable than OEM parts.
- Availability: A wider range of options and faster availability.
- Customization: Options for customization and performance upgrades.
14.2. Disadvantages of Aftermarket Parts
- Compatibility Issues: Potential compatibility issues with the motorcycle model.
- Quality Variability: Quality can vary significantly between different manufacturers.
- Warranty and Support: Limited warranty and support options.
14.3. Consumer Behavior and Preferences
- Price Sensitivity: Many consumers prioritize cost-effectiveness and are willing to choose aftermarket parts.
- Brand Loyalty: Some consumers prefer OEM parts due to brand loyalty and perceived quality.
- Informed Decision-Making: Increasingly, consumers are researching and making informed decisions based on reviews and expert advice.
15. The Role of Cylinder in Motorcycle Performance and Efficiency
The cylinder is the heart of the motorcycle engine, and its performance directly impacts the overall performance and efficiency of the motorcycle. Understanding how the cylinder functions and how to maintain it can help you optimize your motorcycle's performance.
15.1. Cylinder Function and Performance
- Combustion Efficiency: The cylinder is responsible for the combustion process, where fuel and air are mixed and ignited to produce power. The efficiency of this process directly impacts the engine's performance.
- Power Output: The cylinder's design and condition affect the engine's power output. A well-maintained cylinder can deliver better performance and fuel efficiency.
- Smoothness and Reliability: A well-maintained cylinder contributes to a smoother and more reliable engine operation.
15.2. Factors Affecting Cylinder Performance
- Fuel Quality: Using high-quality fuel can help prevent carbon buildup and ensure efficient combustion.
- Cooling System: A properly functioning cooling system is essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures and preventing overheating.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication of the cylinder and piston surfaces is essential to reduce friction and wear.
16. The Impact of Cylinder on Fuel Efficiency and Emissions
The cylinder's design and performance have a significant impact on fuel efficiency and emissions. A well-maintained cylinder can help reduce fuel consumption and emissions.
16.1. Fuel Efficiency
- Combustion Efficiency: A well-maintained cylinder ensures efficient combustion, which reduces fuel consumption.
- Engine Load: The cylinder's ability to handle engine load affects fuel efficiency. A well-maintained cylinder can handle load more efficiently, reducing fuel consumption.
16.2. Emissions
- Emissions Control: A well-maintained cylinder helps reduce emissions by ensuring efficient combustion and reducing unburned fuel.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting emissions standards is essential for compliance with environmental regulations.
17. The Role of Cylinder in Motorcycle Safety
The cylinder is a critical component of the motorcycle engine, and its performance directly impacts the safety of the rider. A well-maintained cylinder can help ensure the motorcycle operates safely and reliably.
17.1. Safety Considerations
- Engine Reliability: A well-maintained cylinder ensures the engine operates reliably, reducing the risk of mechanical failure.
- Performance Consistency: A well-maintained cylinder ensures consistent performance, reducing the risk of unexpected behavior.
- Rider Confidence: A well-maintained cylinder can help build rider confidence and reduce the risk of accidents.
18. The Role of Cylinder in Motorcycle Customization and Racing
For enthusiasts and racers, the cylinder is not just a functional component but also a key element in customization and performance tuning. Understanding how the cylinder can be modified and optimized can enhance the riding experience.
18.1. Custom Cylinder Modifications
- Cylinder Porting and Polishing: Modifying the cylinder bore and ports can improve airflow and combustion efficiency, leading to increased power output.
- Cylinder Head Modifications: Modifying the cylinder head can improve combustion efficiency and power output.
- Cylinder Liners and Sleeves: Replacing or upgrading cylinder liners can improve durability and performance.
18.2. Racing Applications
- High-Performance Cylinders: Racing motorcycles often use specialized cylinders designed for high-performance applications, with features such as reinforced cylinder walls and optimized combustion chambers.
- Cooling Systems: Enhanced cooling systems are essential for high-performance cylinders to prevent overheating and ensure reliability.
- Lightweight Materials: The use of lightweight materials can reduce weight and improve performance.
18.3. Customization and Personalization
- Aesthetic Customization: Custom cylinders can be designed with unique finishes, colors, and designs to match the rider's personal style.
- Performance Upgrades: Custom cylinders can be designed to enhance performance, such as increased power output and improved fuel efficiency.
19. The Role of Cylinder in Motorcycle Maintenance and Longevity
Proper maintenance of the cylinder is essential for ensuring the longevity and performance of the motorcycle. Understanding the importance of regular maintenance can help prevent costly repairs and ensure the motorcycle operates reliably.
19.1. Regular Maintenance
- Oil Changes: Regular oil changes are essential to ensure proper lubrication and reduce wear on the cylinder and other engine components.
- Cooling System Maintenance: Regularly check and maintain the cooling system to ensure optimal operating temperatures.
- Air Filter Replacement: Replace air filters regularly to ensure clean air intake and prevent carbon buildup.
19.2. Diagnostic and Preventive Maintenance
- Compression Test: Regular compression tests can help identify issues with the cylinder, such as worn piston rings or leaking head gaskets.
- Visual Inspections: Regular visual inspections can help identify signs of wear, such as cracks, leaks, or carbon buildup.
- Diagnostic Tools: Using diagnostic tools such as a multimeter or engine analyzer can help identify electrical or mechanical issues.
19.3. Preventive Maintenance Tips
- Follow the Service Schedule: Follow the manufacturer's recommended service schedule for regular maintenance.
- Use Quality Parts and Fluids: Use high-quality parts and fluids to ensure longevity and reliability.
- Professional Maintenance: Consider professional maintenance for complex repairs or when unsure about the issue.
20. The Enduring Importance of Motorcycle Cylinders
Motorcycle cylinders are a critical component of motorcycle engines, influencing performance, durability, and environmental impact. Understanding the design, function, and maintenance of cylinders is essential for riders, mechanics, and enthusiasts alike. As the industry evolves, continued innovation and consumer education will play a key role in shaping the future of motorcycle technology.
21. The Role of Cylinder Design in Engine Performance
The design of the motorcycle cylinder plays a critical role in the overall performance of the engine. The shape, size, and material of the cylinder can influence power output, fuel efficiency, and durability.
Cylinder Bore and Stroke
The bore (diameter of the cylinder) and stroke (length of the piston's travel) are key parameters that determine the engine's displacement and power characteristics. A larger bore can allow for more air-fuel mixture, leading to higher power output, while a longer stroke can improve torque.
Cylinder Head Design
The cylinder head design affects the airflow into and out of the cylinder. A well-designed cylinder head can improve combustion efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance engine performance.
Cylinder Cooling
Proper cooling is essential for maintaining engine temperature. Overheating can lead to cylinder damage, reduced performance, and engine failure. Cooling systems, such as liquid cooling or air cooling, are used to regulate engine temperature.
22. The Future of Motorcycle Cylinder Technology
The future of motorcycle cylinder technology is shaped by ongoing innovation, technological advancements, and changing consumer demands. Several key trends are expected to influence the industry in the coming years.
22.1. Advanced Materials and Manufacturing
- Lightweight Materials: The use of lightweight materials such as aluminum, composites, and carbon fiber is becoming more common, leading to lighter and more efficient engines.
- Additive Manufacturing: 3D printing and other additive manufacturing techniques are being explored for producing complex and customized cylinder designs.
22.2. Smart Technology Integration
- Smart Sensors and IoT: Integration of sensors and Internet of Things (IoT) technology into cylinders can enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and performance optimization.
- Data-Driven Maintenance: Data from sensors can be used to predict and prevent potential issues before they occur.
22.3. Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Designs
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Increasing use of renewable and sustainable materials in cylinder manufacturing.
- Energy Efficiency: Focus on improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions through advanced cylinder designs.
22.4. Customization and Personalization
- Custom Cylinder Designs: Growing demand for custom and personalized cylinder designs, especially in the custom and racing motorcycle markets.
- Modular Design: Modular cylinder designs that allow for easier customization and upgrades.
Motorcycle cylinders are a complex and vital component of motorcycle engines. While they may seem technical, understanding their function, maintenance, and market dynamics can help you make informed decisions and ensure the performance and longevity of your motorcycle. Whether you are a casual rider or a dedicated enthusiast, knowledge of motorcycle cylinders is a valuable asset in your journey with motorcycles.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى