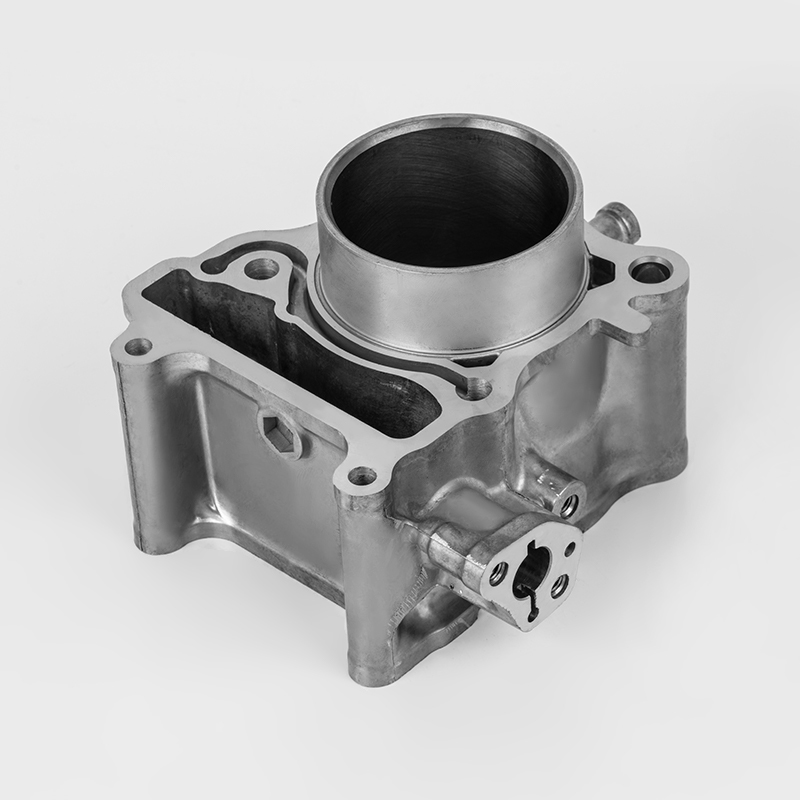
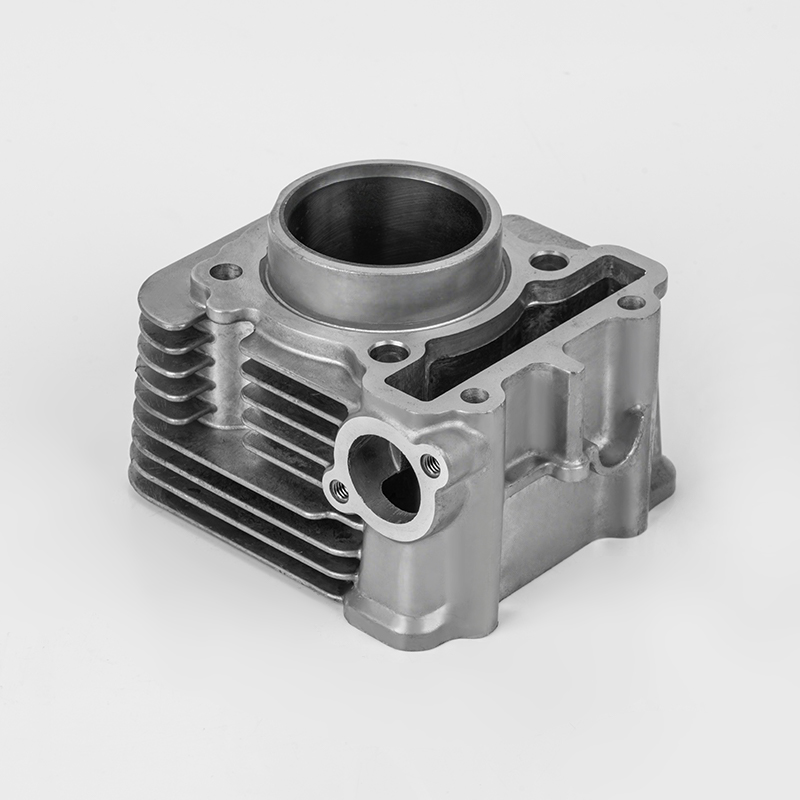
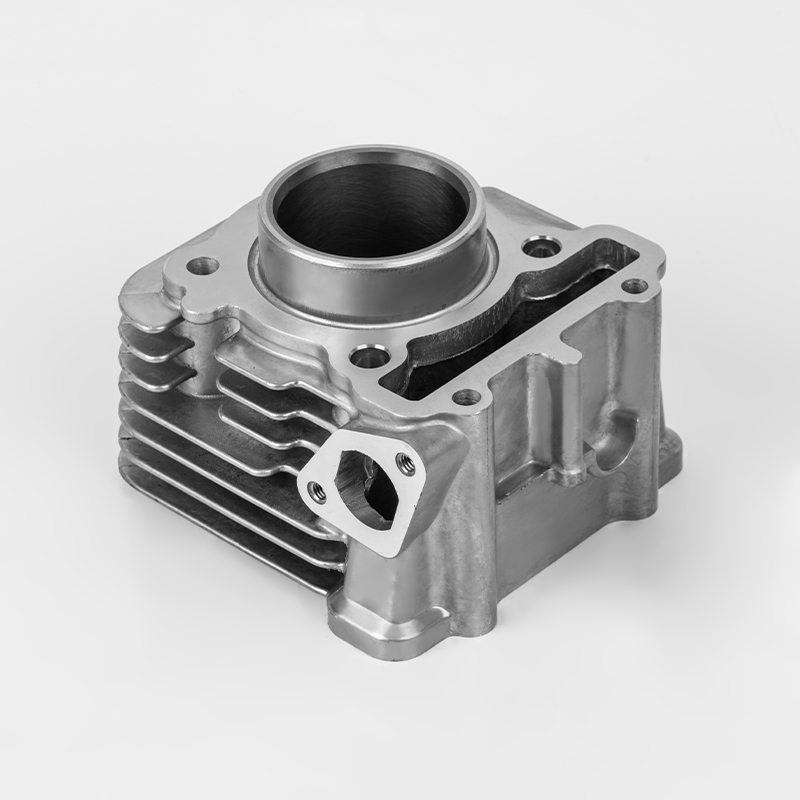
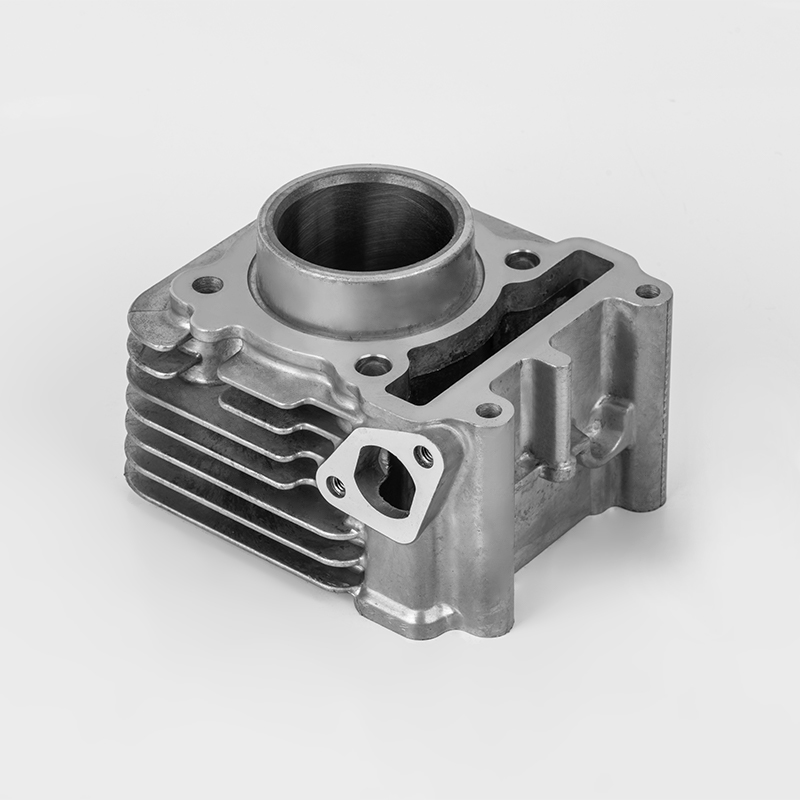
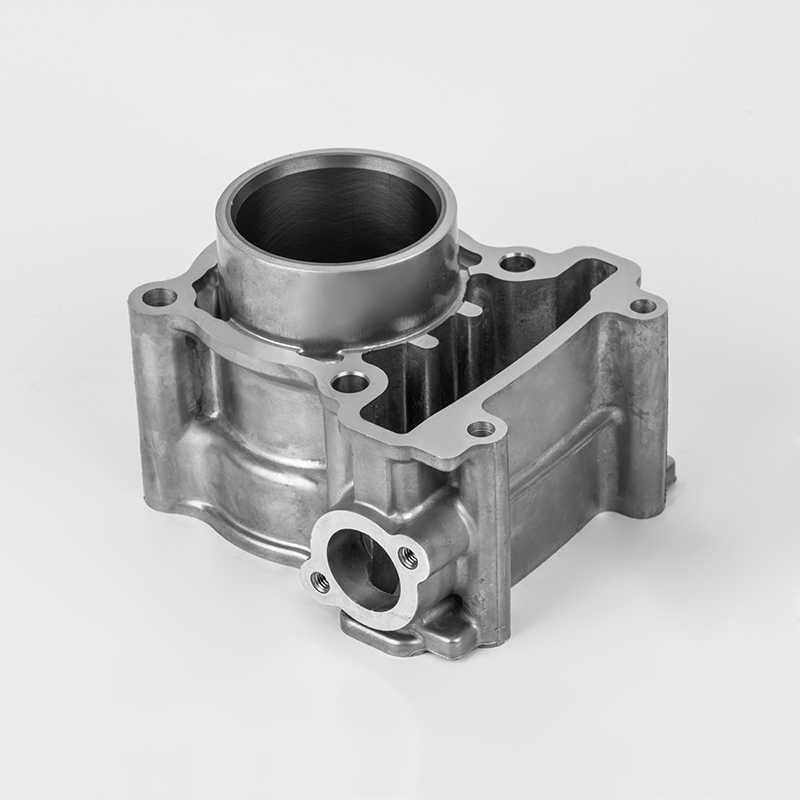
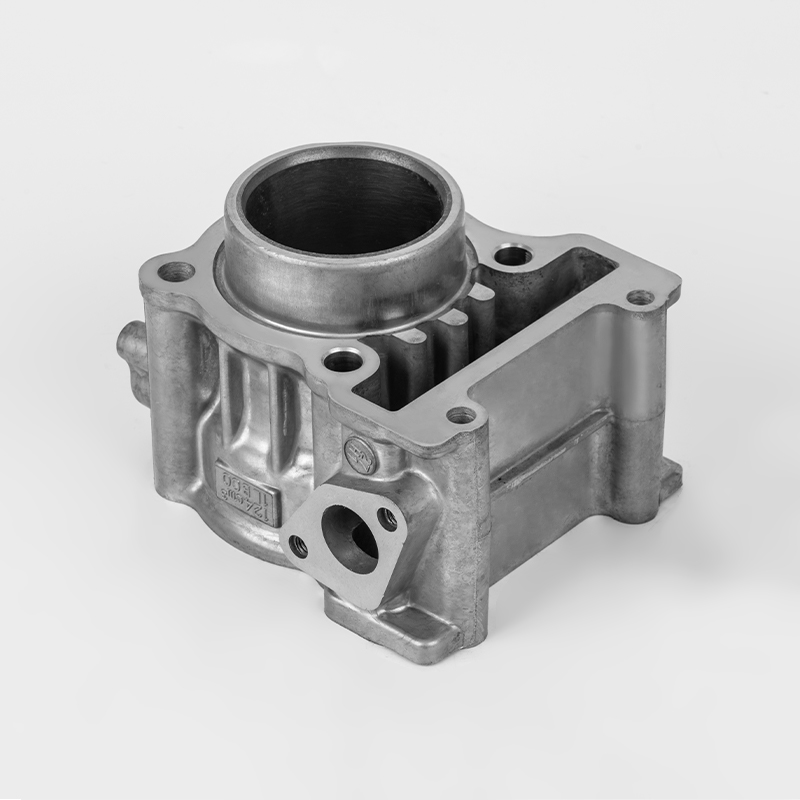
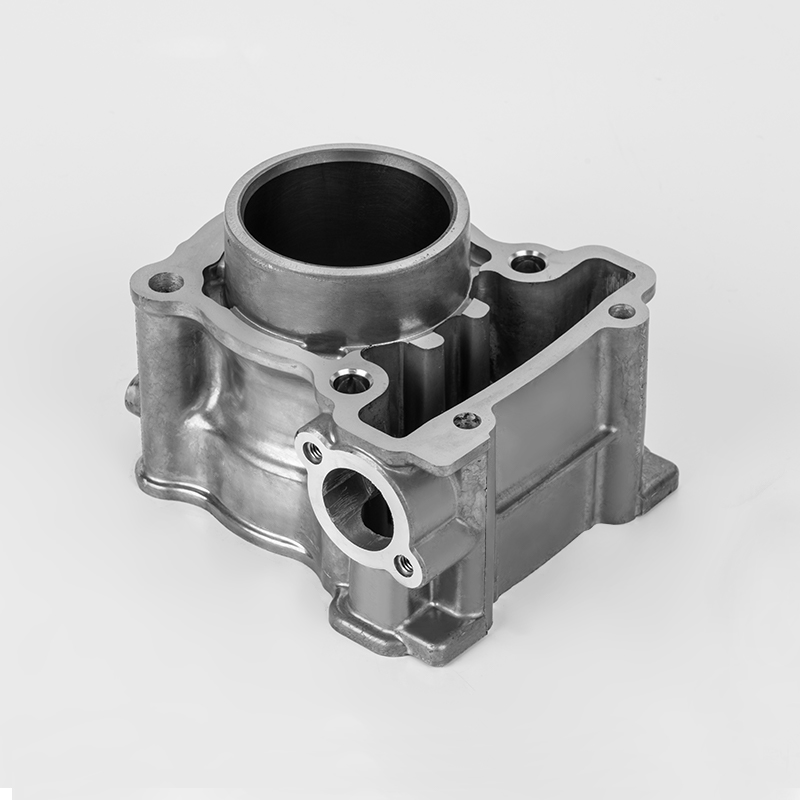
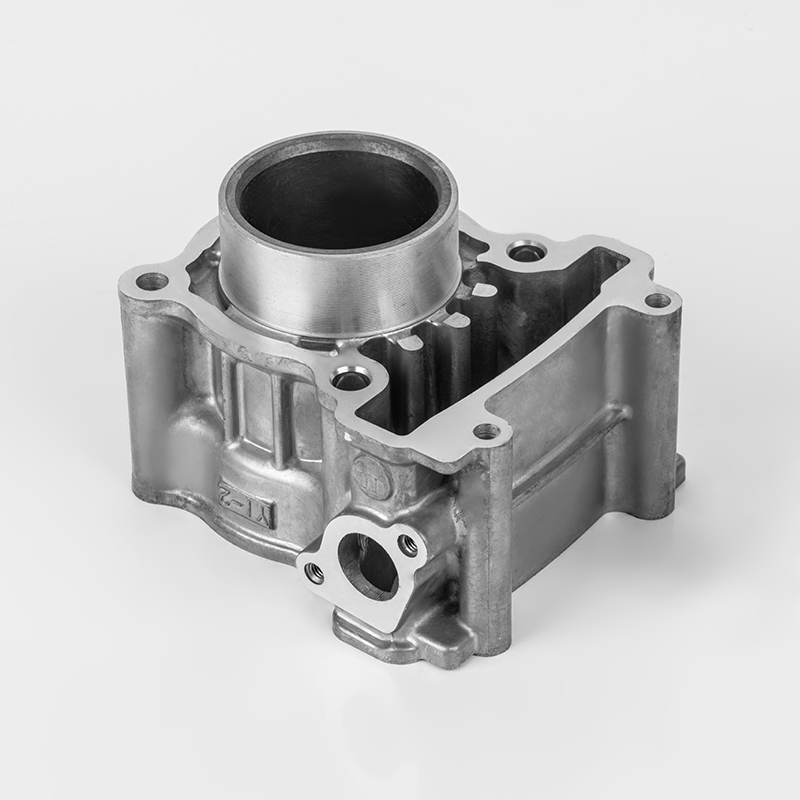
Motorcycle cylinder is a key component of the engine. Here's a breakdown of its role and features:
Function – The cylinder is where fuel combustion occurs, converting energy into motion by driving the piston.
Material – Typically made from durable metals like aluminum or cast iron to withstand high heat and pressure.
Design – Usually cylindrical in shape, with a smooth inner surface (bore) to allow the piston to move efficiently.
Cooling – Often includes cooling fins (air-cooled) or water jackets (liquid-cooled) to manage engine temperature.
Part of the Block – May be part of a larger engine block in multi-cylinder designs (e.g., inline, V-twin).
Wear Resistance – The inner wall is often coated or treated to reduce friction and prolong engine life.
Connection to Other Parts – Works with the piston, valves, and spark plug to complete the combustion cycle.
| Aspect | Description |
| Function | Houses the combustion process, converting fuel energy into piston movement. |
| Material | Typically aluminum or cast iron for heat and pressure resistance. |
| Design | Cylindrical shape with a smooth bore for piston movement. |
| Cooling | Uses fins (air-cooled) or water jackets (liquid-cooled) to dissipate heat. |
| Engine Block | May be part of a single or multi-cylinder configuration (e.g., V-twin). |
| Wear Resistance | Inner surface often coated to minimize friction and extend lifespan. |
| Key Connections | Links to pistons, valves, and spark plugs for combustion cycle operation. |

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى